Reactivity Series of Metals and Nonmetals
The reactivity series is a systematic arrangement of metals and nonmetals in order of their decreasing chemical activity.
Also known as the activity series, it helps predict how a substance will react with others, particularly in displacement reactions.
This series determines the ability of a metal to replace another in a reaction and indicates how it interacts with oxygen, water (cold, hot, or steam), and acids.
Chemistry revolves around chemical reactions, where substances interact to form new products through transformative processes.
Element reactivity varies based on their position in the reactivity series, a key concept for understanding chemical processes.
This post will explore the significance of the reactivity series, how it influences chemical reactions, and its practical applications in everyday life. Let’s dive in!
METAL REACTIVITY SERIES
Definition of metal reactivity series –
Metal reactivity series is a list in which metals are arranged in the decreasing order of their chemical activity.
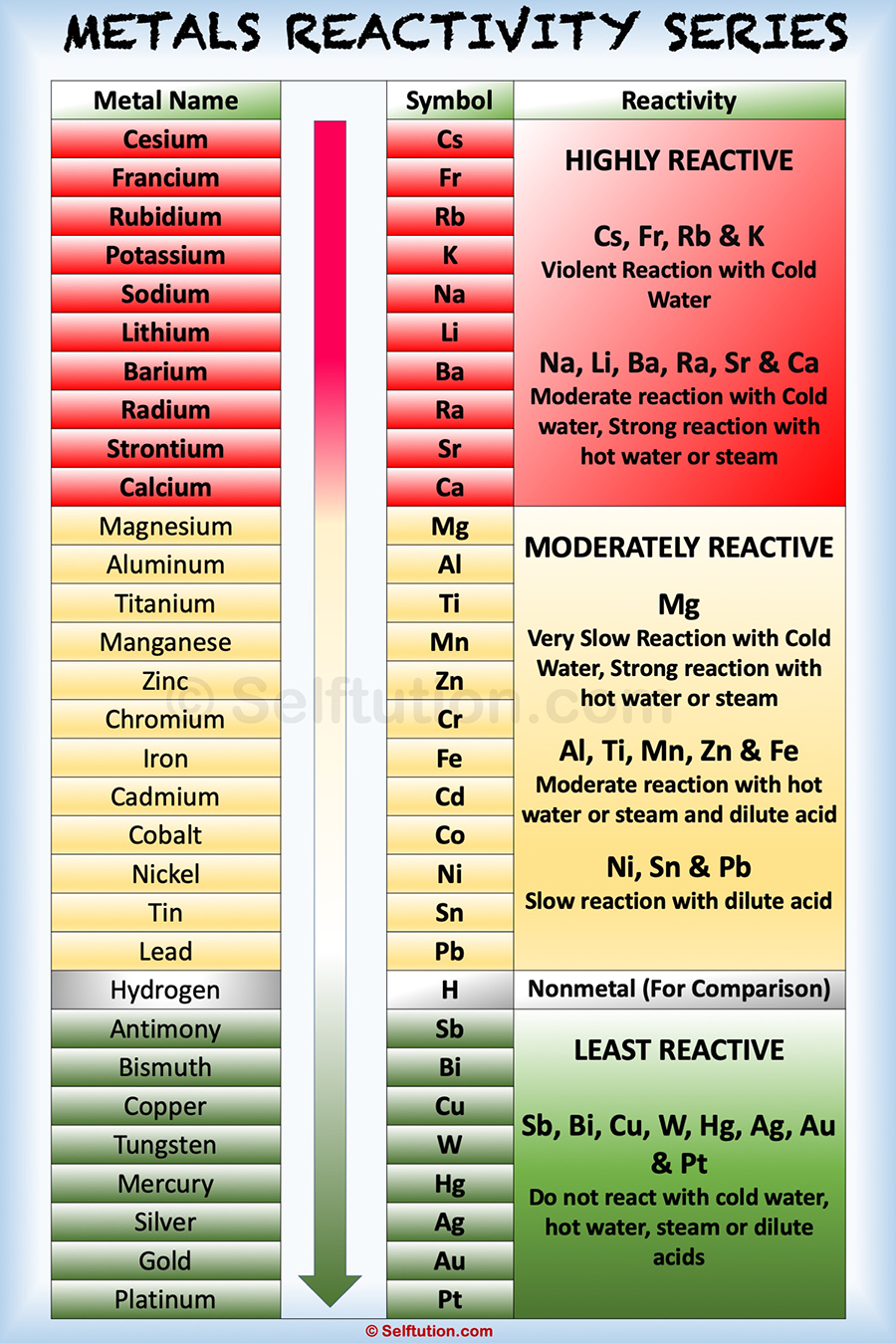
Reactivity Series of Metals
The metal activity or reactivity series finds its utility in the study of displacement reactions. It helps us to predict whether a particular metal can displace another metal from a compound or not.
In a displacement reaction, a metal higher up in the reactivity series displaces all other metals in a compound, which lies below it. For example, zinc being more active than copper replaces it with copper sulfate in the solution state to form zinc sulfate and free copper.
The activity of a metal depends upon its capability to lose electrons in the solution state to form positive ions. The more readily metal loses its electrons, the more active it is, and the higher up it is in the reactivity series. Among the most commonly known metals, the most active cesium is at the top and the least active platinum is at the bottom of the reactivity series.
Special Features of the Reactivity or Activity Series of Metals:
- The ease with which a metal in solution loses electrons and forms a positive ion decreases down the series, i.e., from cesium to platinum.
- Although a non-metal, hydrogen is included in the reactivity series of metals. It is because, like metals, it too loses an electron and becomes a positively charged (H+) ion.
- Metals at the top of the reactivity series have the ability to displace metals that are placed lower from their salt solutions.
- The activity series facilitates the comparative study of the metals in terms of the degree of their reactivity.
- Metals at the top of the reactivity series are difficult to obtain from their ores.
The table below explains the reactions of metals with oxygen (air), water, dilute acids, and other salt solutions, at various levels of the reactivity series.
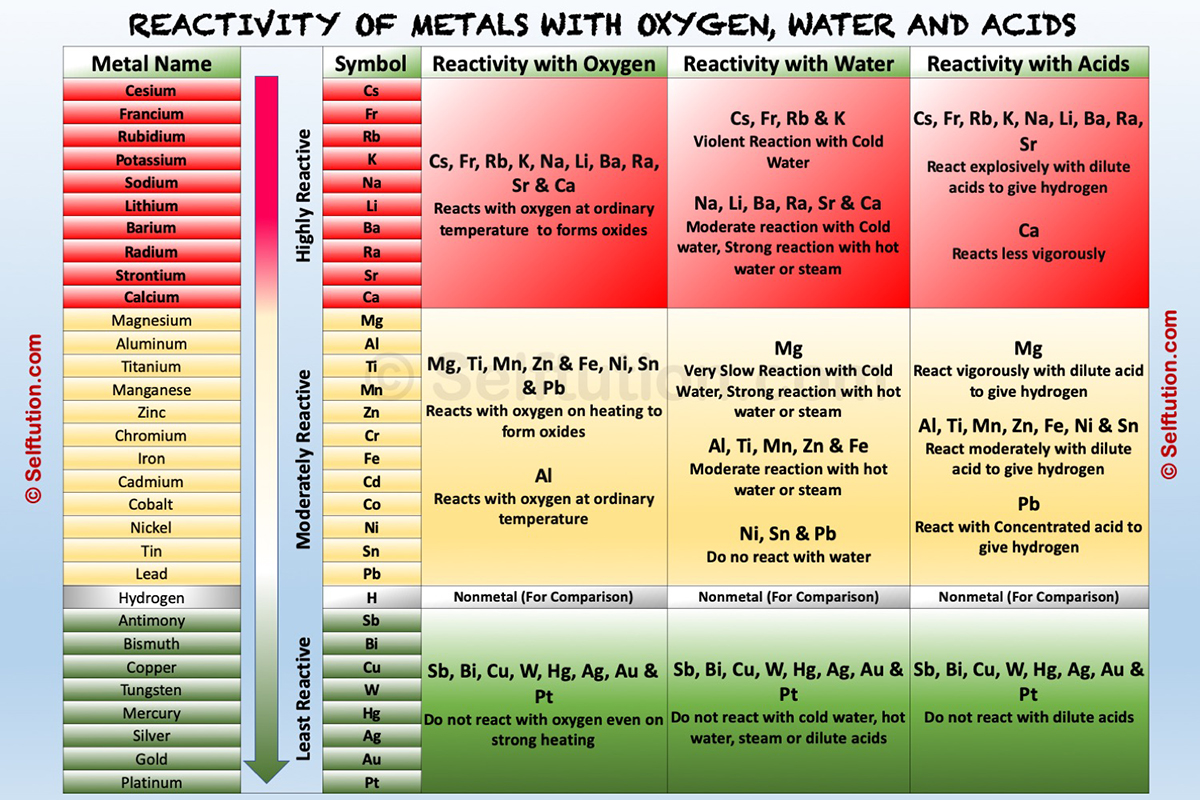
Reactivity of metals with oxygen, water, and acids
NONMETAL REACTIVITY OR ACTIVITY SERIES
Definition of reactivity of nonmetals–
Nonmetal activity series is a list in which nonmetals are arranged in the decreasing order of their reactivity.
Similar to metals, we can also arrange nonmetals in terms of their reactivity. During displacement reactions, a more active nonmetal displaces a less active nonmetal from a compound.
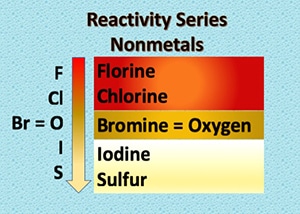
Reactivity Series of Nonmetals
The activity of a nonmetal depends upon its capability to gain electrons in the solution state to form positive ions. The more readily a nonmetal gains electrons, the more active it is, and the higher up it is in the reactivity series.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Which is the most active or reactive metal?
Ans. Cesium and francium are the most reactive metals and are at the top of the reactivity series. However, the quantity of francium produced until now is too small. Therefore, for all practical purposes, we consider cesium as the most reactive metal.
Cesium reacts with water. Video by Periodic Videos
Q2. Which is the least active or reactive metal?
Ans. Platinum is one of the least reactive metals and therefore lies at the bottom of the reactivity series. It has remarkable resistance to corrosion, even at high temperatures, and is therefore considered a noble metal. Due to its low reactivity, it found uses in the manufacture of laboratory equipment, electrodes, platinum resistance thermometers, dentistry equipment, and jewelry.
Q3. Which is the most active or reactive nonmetal?
Ans. Fluorine is the most active nonmetal, and it displaces all other nonmetals in salt solutions.
Q4. What determines the reactivity of metals?
Ans. We determine the reactivity of metals based on their capability to lose electrons in the solution state to form positive ions or cations. Therefore, the more readily metal loses its electrons, the more active it is, and the higher up it is in the reactivity series.
Q5. What determines the reactivity of nonmetals?
Ans. We determine the reactivity of nonmetals based on their capability to gain electrons in the solution state to form negatively charged ions or anions. Therefore, nonmetals that gain electrons rapidly are more active than others.
Knowledge of chemistry is endless, so to know more about various types of chemical reactions. Click here