Types of Chemical Reactions in Chemistry with Examples
Master the 4 Major Types of Chemical Reactions with Clear Examples & Simple Explanations | Selftution.com
Selftution.com is the best educational website for students, offering step-by-step guides to make chemistry easy. Learn decomposition, combustion, single & double displacement reactions with real-world examples.
Welcome to Selftution.com – Where complex science becomes simple! So, let’s begin.
Chemical reactions occur all around us, from burning wood to digesting food.
They involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, leading to new substances with different properties.
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are different types of chemical reactions, such as hydrolysis, oxidation, synthesis, reduction, combustion, electrolysis, and neutralization.
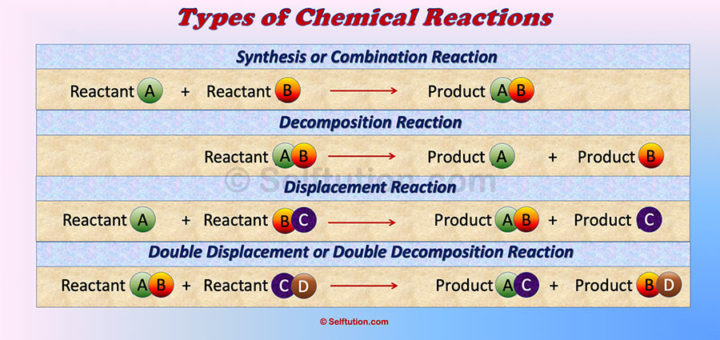
However, all chemical reactions can be grouped into four main categories:
- Combination or synthesis reaction
- Decomposition reaction
- Displacement reaction, and
- Double displacement or double decomposition reaction
Types of chemical reactions in chemistry with examples
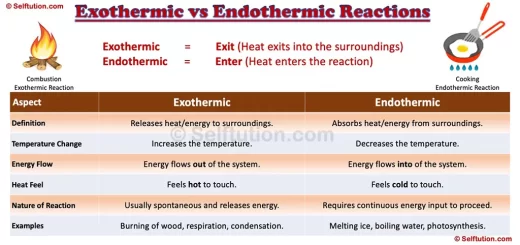
Additionally, we can classify chemical reactions based on energy changes. Exothermic reactions release energy in the form of heat or light, whereas endothermic reactions absorb energy.
Before we study various types of reactions, it is important to know what a chemical reaction is.
WHAT IS A CHEMICAL REACTION?
A chemical reaction is a process in which two or more substances, when brought into close contact with each other, interact chemically to produce one or more new substances.
Definition of a chemical reaction –
A chemical reaction is a process in which two or more substances called reactants, react with each other to form one or more new substances called products. This may involve the evolution or absorption of energy.
Reactant (A) + Reactant (B) → Product (C) + Product (D)
COMBINATION OR SYNTHESIS CHEMICAL REACTIONS
A chemical reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single new substance is called a combination or synthesis reaction. For example,
A + B → AB
In the above reaction, a combination of substances A & B (reactants) takes place to give a molecule of a new substance AB (product). It’s important to note that most of the synthesis reactions are exothermic.
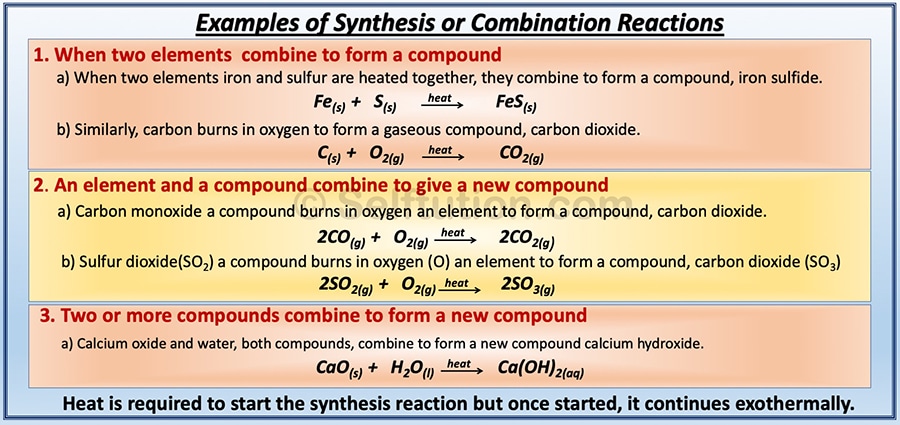
There are three types of combination or synthesis chemical reactions:
- Two elements combine to form a compound.
- An element and a compound combine to give a new compound.
- Two or more compounds combine to form a new compound.
Examples of all three types of combination or synthesis chemical reactions:
Types of synthesis or combination chemical reactions with examples
DECOMPOSITION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
A decomposition reaction is one in which a compound splits into simpler substances (elements or compounds) such that the products formed do not recombine to form the original compound. For example,
AB → C + D
Here, the decomposition of the molecule AB takes place to give two or more new substances, C & D. It may occur in the presence of heat or light or by the passage of an electric current. Therefore, decomposition reactions are of three types –
- Thermal decomposition,
- Photo decomposition or photolysis, and
- Electrolysis
Thermal decomposition reactions are those that involve heat. Photo decomposition or photolysis is the process that involves light. Electrolysis is due to the passing of an electric current.
Heat, light, and electricity are different forms of energy that cause the breaking of bonds in the molecules of reactants to yield simpler products. Therefore, decomposition reactions are endothermic.
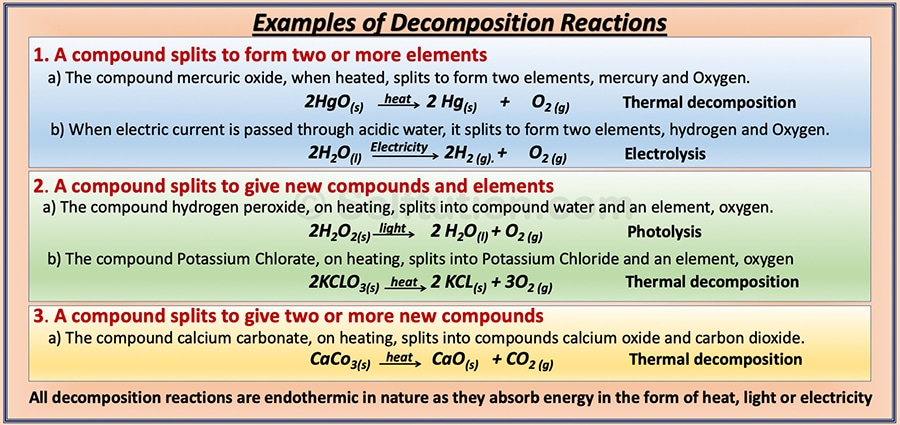
Similar to combination reactions, based on the types of products formed, decomposition chemical reactions are also of three types:
- A compound breaks up to form two or more elements.
- Formation of both elements and compounds due to the breakup of a compound.
- A compound breaks up to form two or more compounds.
Examples of all types of chemical decomposition reactions:
Types of decomposition chemical reactions with examples
DISPLACEMENT CHEMCIAL REACTIONS
In a displacement reaction, a more active element displaces a less active element from a compound. In such reactions, the active element replaces one element of the reactant molecule. For example,
AB + C → CB + A
Here, C displaces A from AB, since C is chemically more active as compared to A. A displacement reaction can be exothermic or endothermic in nature. We used the reactivity series of metals and nonmetals to identify the chemical activity of an element. In the reactivity series, more active metals are at the top and less active at the bottom.
There are three types of displacement reactions:
- A more reactive metal displaces a less active metal from its salt solution.
- A metal more reactive than hydrogen displaces hydrogen gas from an acid.
- A more reactive non-metal displaces a less active non-metal from its salt solution.
Examples of types of chemical displacement reactions:
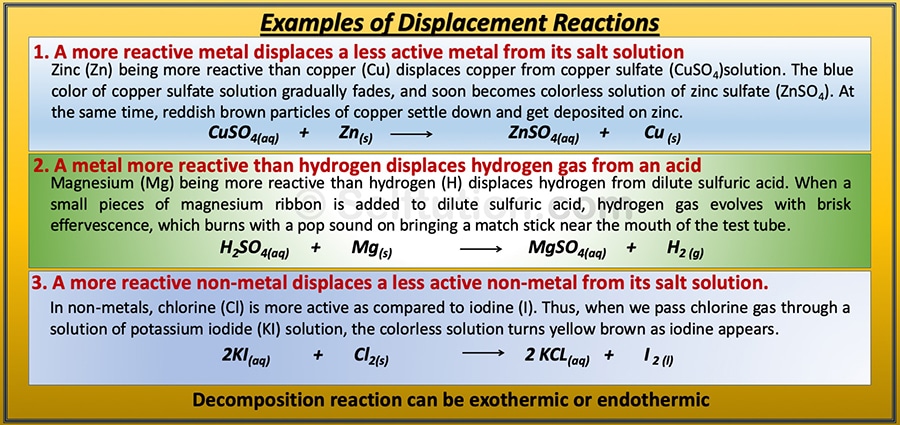
Types of displacement chemical reactions with examples
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT OR DOUBLE DECOMPOSITION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
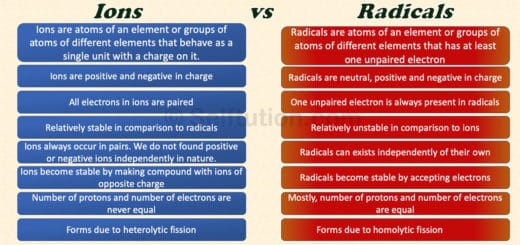
This is a type of chemical reaction in which two compounds in a solution state exchange their ions or radicals to form new compounds. For example,
AB + CD → CB + AD
Here, AB & CD are the two reactant molecules. They exchange their ions or radicals to form two new molecules, CB and AD. Double displacement or double decomposition reactions are of two types: precipitation reactions and neutralization reactions.
- Precipitation reaction: A chemical reaction in which two compounds in their aqueous state react to form an insoluble solid (a precipitate) as one of the products is called a precipitation reaction.
- Neutralization reaction: A chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base or an alkali to form a salt and water is called a neutralization reaction.
Examples of types of double displacement or double decomposition chemical reactions for precipitation and neutralization reactions:
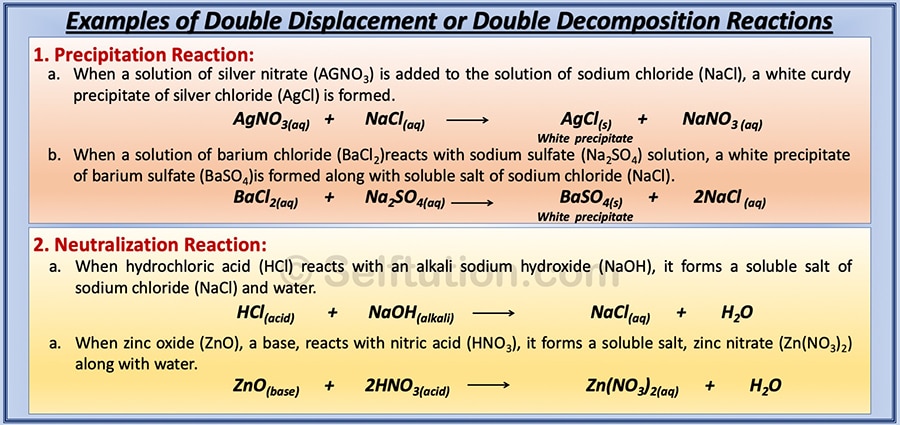
Types of double displacement or decomposition chemical reactions with examples
Back to >>Types of chemical reactions