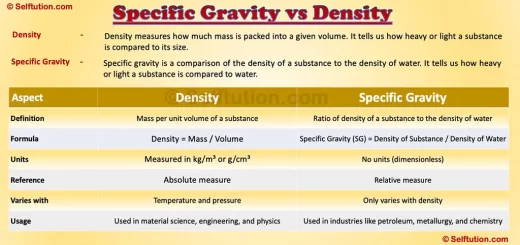
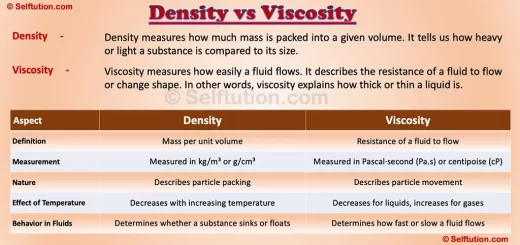
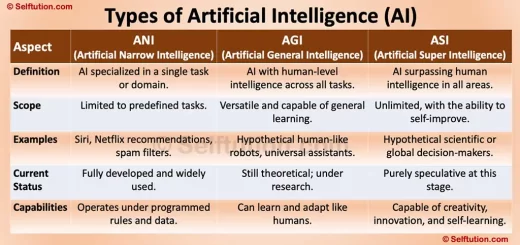
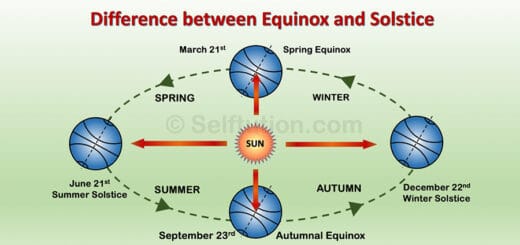
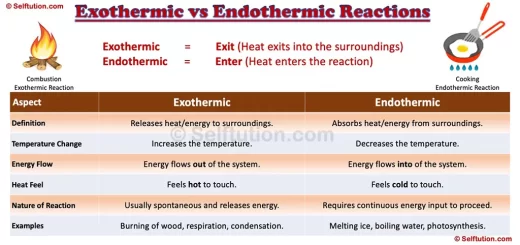
How Stars Are Formed: Key Stages of Their Formation
Stars are the shining lights in the night sky, fascinating and mysterious. But have you ever wondered how stars are formed? The process is complex and beautiful, taking place over millions of years. In this blog, we will explore the key stages of star formation. By the end, you’ll know all about how stars are formed.
Introduction to Star Formation
Key Stages of Star Formation
1. Nebula: The Birthplace of Stars
Stars are formed in a special place in space called a nebula. A nebula is like a giant cloud, mostly made of hydrogen gas, with a bit of helium and tiny amounts of other elements. These clouds are incredibly huge and can stretch across many light-years. For the latest pictures of some famous nebulae. Click….Nasa Gallery
Key Points:
- Nebula Composition:
- Hydrogen: The main ingredient in a nebula.
- Helium: There is also some helium.
- Other Elements: There are tiny amounts of heavier elements too.
Size and Scale:
- Enormous Size: Nebulae can be several light-years across.
- Star Factories: They contain enough material to create thousands of stars.
In simple terms, imagine a nebula as a massive, colorful cloud floating in space. This cloud has all the ingredients needed to make new stars. Over time, parts of the nebula can collapse under gravity, getting hotter and denser, until new stars are formed. So, nebulae are like cosmic nurseries where stars come to life.
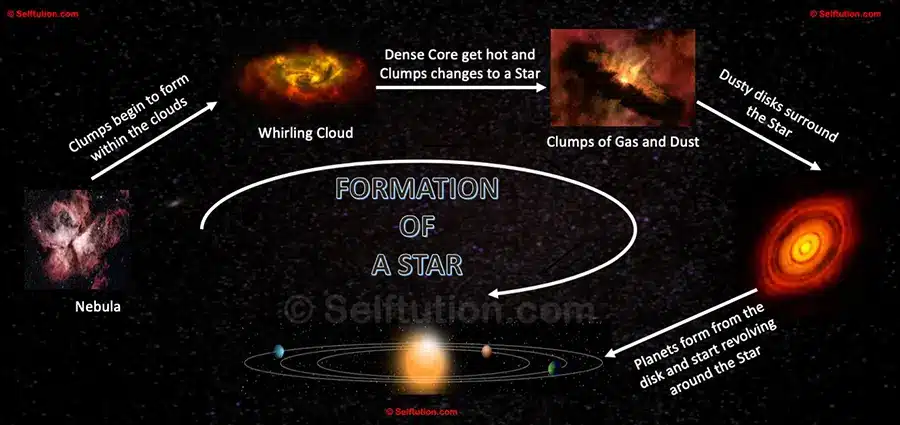
Stages of Star Formation
2. Gravitational Collapse
In the process of star formation, after a star’s birthplace nebula, comes to the next important stage called gravitational collapse. Here’s what happens:
- Initial Collapse:
- Small Regions Shrink: Small areas shrink inside the giant nebula because of gravity. Gravity is the force that pulls objects toward each other; in this case, it pulls parts of the nebula together.
- Increasing Density and Temperature:
- Becoming Denser: As these small regions get pulled together, they become more packed with material.
- Heating Up: As they get denser, they also get hotter.
Imagine parts of the nebula as small clumps of dust and gas that start to get squeezed together by an invisible hand (gravity). As they get squeezed, these clumps grow tighter and warmer. Consequently, this squeezing and heating process is crucial because it sets the stage for the formation of new stars. Therefore, gravitational collapse is like the nebula’s way of turning on the oven to start baking stars!
3. Formation of Protostars
After the stage of gravitational collapse, we move to the next step in star formation: the formation of protostars. Here’s how it happens:
- Formation of Protostars:
- Collapsing Regions Form Protostars: As the small, dense, and hot regions within the nebula continue to shrink, they become protostars. Think of protostars as baby stars—they’re not fully formed yet but are on their way.
- Accretion:
- Gathering More Material: Protostars still pull more gas and dust from the surrounding nebula. This process is called accretion. As they gather more material, they grow more massive.
So, protostars are like stars in the making. They are in the early stages of their life, still accumulating mass and getting ready to shine brightly in the sky. This stage is crucial as it sets the foundation for the star’s future.
4. Nuclear Fusion Ignites
The important but not the last key stage in the formation of a star is when nuclear fusion begins. Here’s what happens:
- Increasing Temperature and Pressure:
- Hotter and Denser Protostar: As the protostar continues to gather material, it gets hotter and denser. The pressure in its core builds up.
- Temperature Threshold:
- Reaching 10 Million Degrees Celsius: When the core temperature hits about 10 million degrees Celsius, something incredible happens.
- Nuclear Fusion Begins:
- Fusion Process: At this extremely high temperature, hydrogen atoms combine to form helium. This process is called nuclear fusion.
- Energy Release: Nuclear fusion releases a huge amount of energy. This energy makes the star shine.
Think of nuclear fusion as the “switch” that turns a protostar into a full-fledged star. It’s like lighting a cosmic furnace. Once nuclear fusion starts, the star begins to shine brightly, and it can continue shining for millions or even billions of years. This process is what powers stars and gives them their light and heat.
5. Star Stabilization
Once nuclear fusion starts, the star moves into a phase called stabilization. This is a crucial stage where the star finds a balance and remains stable for most of its life. Here’s how it works:
- Outward Pressure vs. Inward Gravity:
- Energy from Fusion: The nuclear fusion process produces a lot of energy. This energy creates an outward pressure that pushes against the star’s outer layers.
- Inward Pull of Gravity: Simultaneously, gravity pulls the star’s material inward, trying to make it collapse.
- Balance Achieved:
- Stable Star: The outward pressure from the energy produced by fusion balances the inward pull of gravity. This balance keeps the star stable and prevents it from collapsing or expanding uncontrollably.
- Main Sequence:
- Long Stable Period: After reaching this balance, the star enters the main sequence stage. During this time, the star steadily burns hydrogen in its core, maintaining its stability.
- Most of Its Life: The star will spend most of its life in this main sequence phase, shining brightly and steadily.
In summary, star stabilization is like a cosmic tug-of-war where neither side wins. Specifically, the energy from fusion pushes out, while gravity pulls in. Consequently, these forces balance each other perfectly, allowing the star to stay stable and shine consistently for a very long time. This balance keeps stars like our Sun stable and shining for billions of years.
The Importance of Star Formation
Understanding how stars are formed is crucial for several reasons. Stars are the building blocks of galaxies. They provide the energy needed for life and create the elements necessary for planets and living organisms.
- Galactic Building Blocks: Stars make up galaxies and influence their structure.
- Energy for Life: Stars provide the light and heat necessary for life to exist.
- Element Creation: Stars produce the elements that make up planets and living things.
Conclusion
In summary, stars are formed through fascinating stages, starting from a nebula and ending as stabilization. Each stage plays a crucial role in the star’s development and eventual fate. By understanding these stages, we gain insight into the life cycle of stars and the incredible processes that shape our universe.
To recap, here are the key stages of how stars are formed:
- Nebula: The birthplace of stars.
- Gravitational Collapse: Regions of the nebula collapse under gravity.
- Formation of Protostars: Early stars gather material and grow.
- Nuclear Fusion Ignites: Fusion of hydrogen into helium begins.
- Star Stabilization: The balance of forces keeps the star stable.
Now you know how stars are formed, from the initial cloud of gas and dust to the final stages of their life. This incredible journey spans millions of years and involves some of the most powerful forces in the universe. Next time you look up at the night sky, you can appreciate the amazing process that brought those twinkling lights to life.