Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures | Definition, Examples
In chemistry, we group materials around us into pure substances and mixtures. We further classify mixtures into homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, based on how we distribute their components.
These mixtures are all around us, from the air we breathe to the food we eat.
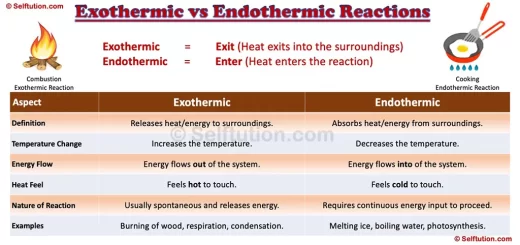
Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition, meaning we evenly distribute their components, while heterogeneous mixtures have visibly different parts. Recognizing these differences helps us better understand the world of materials.
This post will explore the characteristics of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with easy-to-understand examples.
Let’s uncover the science behind these mixtures!
Mixture Definition
A mixture is an impure substance created by combining two or more pure substances (elements or compounds) in any proportion, without undergoing any chemical change, thereby retaining their individual properties.
Most substances we encounter exist in the form of mixtures. The pure substances that combine to form a mixture are called its components or constituents. Mixtures can be created by combining elements, compounds, or both. Depending on the physical state of its components, a mixture can exist in any of the three states of matter: solid, liquid, or gas. Since the components of a mixture do not undergo chemical reactions, they retain their individual properties and can be separated using various physical methods.

Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixture Definition and Examples
Examples of Mixture
Some common examples of mixtures in our daily lives include air, milk, fruit juice, medicines, honey, tap water, brass, and bronze.
Air is a mixture of oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide gases. It also contains water vapor, dust particles, and traces of inert gases.
Mixtures are classified into two types: homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. However, before we delve into studying them, let’s first understand some basic characteristics of mixtures.
Characteristics of Mixtures with Examples
In mixtures, the components are loosely combined and retain their individual properties. Based on this, mixtures exhibit the following characteristics:
- No Chemical Change:
A mixture consists of two or more pure substances that coexist without undergoing any chemical combination. For example, in a mixture of common salt and sand, their particles are not chemically bonded. We can easily separate the salt by dissolving it in water and filtering out the sand. Variable Composition:
The components of mixtures can vary in proportion, making it impossible to represent them with a chemical formula. For instance, you can prepare a mixture of sand and common salt by mixing 1 g of salt with 2 g of sand or 2 g of salt with 2 g of sand.
- No Specific Physical Properties:
A mixture does not have fixed melting or boiling points. Its properties depend on the proportions of its components. For example, the boiling point of water increases as more common salt is dissolved in it. - Homogeneity:
Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. For example, a mixture of salt and water is homogeneous, whereas a mixture of salt and sand is heterogeneous. - Separation:
Simple physical methods can separate the components of a mixture. For instance, evaporation can recover salt dissolved in water. - Energy Change:
Generally, no significant energy change (heat or light) occurs during the formation of mixtures. For example, when sand and salt are mixed, there is no release or absorption of energy.
HOMOGENEOUS AND HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE
Based on their composition and distribution, we can divide mixtures into two types – homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Video courtesy eNotes
HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE
Definition of the homogeneous mixture–
Homogeneous mixture is the one, in which the components are uniformly distributed throughout its volume and cannot be seen separately.
We should not confuse a homogenous mixture with a compound. In compounds, atoms of various elements combine chemically in a fixed ratio. Whereas, in homogeneous mixtures, components of the mixture stay together in a varying ratio. For more differences between mixture and compound, click here.
Examples of Homogeneous Mixture-
A salt solution in water is an example of a homogeneous mixture, as we cannot see salt particles separately from water. We can prepare a salt solution by mixing one or two tablespoons in 1 liter of water. In both cases, the solution formed will be homogeneous, but the proportions of salt and water are not the same.
Some other examples of homogeneous mixtures are – tap water, milk, air, fruit juice, medicine, etc.
We can form a homogeneous mixture of metals by mixing two or more metals in the molten state. This homogeneous mixture of molten metals, on cooling, forms a solid mixture. We call this solid mixture an alloy. For example, brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Similarly, bronze is an alloy of copper, zinc, and tin.
HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE
Definition of the heterogeneous mixture-
A heterogeneous mixture is one in which the components are not uniformly distributed throughout its volume and can be easily distinguished as separate entities.
Examples of Heterogeneous Mixture
Most mixtures found in nature are heterogeneous. For instance, soil is a mixture containing hundreds of elements and compounds, and its composition varies from one location to another. Other examples of heterogeneous mixtures include rocks, a mixture of kerosene and water, and combinations like rice and pulses.
Examples of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
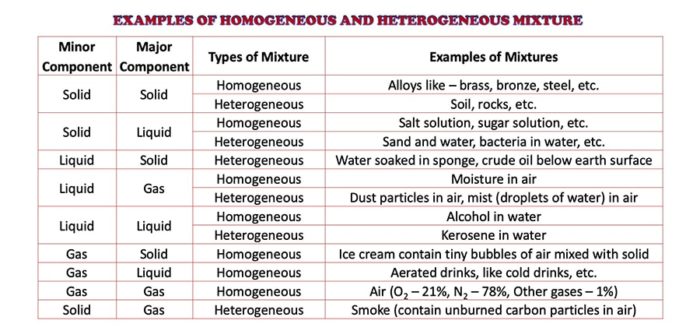
Examples of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures