Difference Between Mixture and Compound With Examples
Mixture vs Compound: Key Differences Explained with Simple Examples | Selftution.com
Learn the fundamental distinctions between mixtures and compounds through clear definitions, comparison charts, and real-world examples.
Welcome to Selftution.com – making chemistry easy to understand! So, let’s begin.
In chemistry, a mixture and a compound represent two different forms of substances. This post will explore these two forms and examine the key differences between a mixture and a compound.
Additionally, we will discuss why water is classified as a compound, while air is considered a mixture.
Skip to >> Why is water a compound and air a mixture?
Definition of a mixture-
The mixture is an impure substance formed by mixing two or more pure substances (elements and compounds) in any proportion, such that they do not undergo any chemical change and retain their individual property.
To learn more about the mixtures, click here
Definition of Compound –
A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio.
To learn more about the compounds, click here
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MIXTURE AND COMPOUND WITH EXAMPLES
Six (6) basic differences between a mixture and a compound are as follows:
01. PURITY
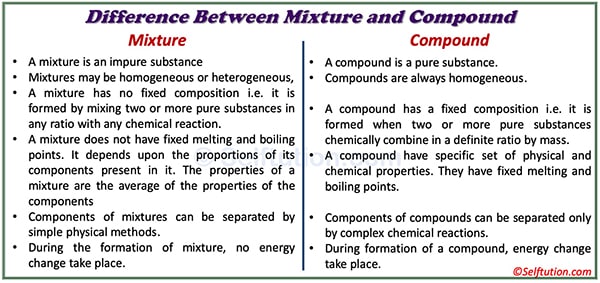
A mixture is an impure substance formed by combining two or more pure substances, whereas a compound is a pure substance.
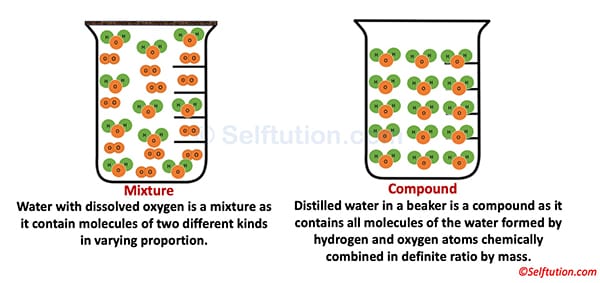
For example, the air is a mixture and therefore an impure substance, as it contains molecules of different gases. It consists of oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), Argon (Ar), water vapor, etc., in varying proportions. In contrast, water (a compound) is a pure substance because it contains only water molecules (H₂O).
02. PROPERTIES
The components of a mixture do not combine chemically; therefore, they retain their chemical and physical properties. In contrast, a compound is a completely new substance with properties entirely different from those of its components.
For example, a water molecule (H₂O) consists of two hydrogen (H) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. Water exists as a liquid under normal conditions, whereas hydrogen and oxygen are gases. A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen, when ignited, produces fire, whereas water is commonly used to extinguish fire.
03. HOMOGENEITY
The mixture may be either homogeneous or heterogeneous, whereas a compound is always homogeneous because it consists of molecules of the same kind.
For example, water has uniform properties throughout, making it homogeneous. Similarly, a mixture of salt and water is homogeneous, whereas a mixture of rice and pulses is heterogeneous.
04. COMPOSITION
In mixtures, the ratio of components can vary. Whereas in the case of a compound, the components are present in a fixed ratio by weight.
For example, we can prepare a mixture of sand and common salt either by mixing 1 gm of salt with 2 gm of sand, or 2 gm of salt with 2 gm of sand. Whereas, we get water, a compound, only when hydrogen and oxygen atoms combine chemically in a fixed ratio of 1:8 by mass.
05. SEPARATION
We can separate components of a mixture by simple physical methods. Whereas we cannot separate the components of a compound by simply physical means. In compounds, chemical bonds join atoms together. These bonds are very strong and difficult to break. Thus, to get original elements (or atoms) from compounds, we need to apply chemical methods.
For example, we can separate salt from the salt solution simply by evaporation. Whereas, to break the molecule of water into its elements, hydrogen and oxygen, we need to pass an electric current through it.
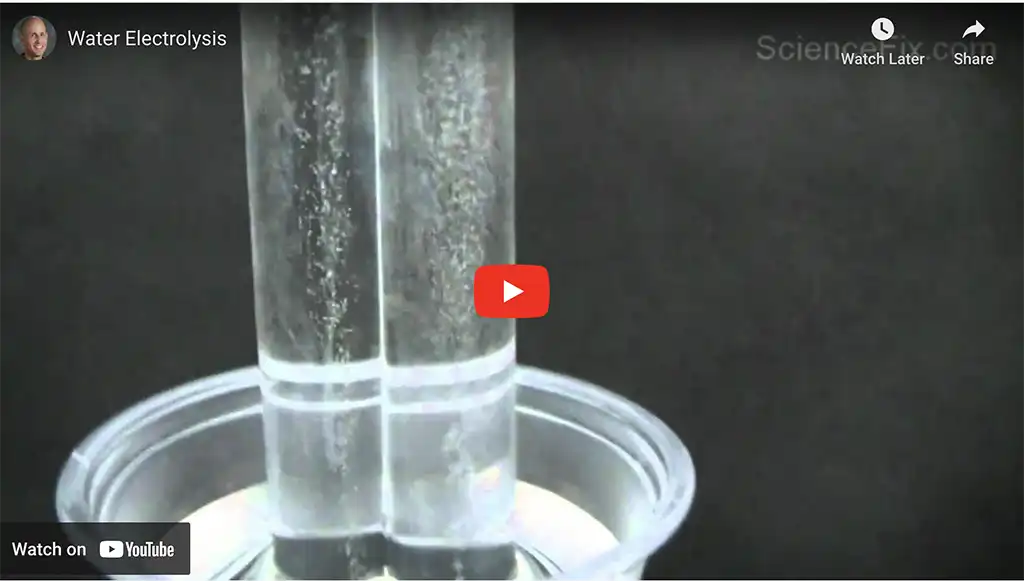

Interesting home experiment by sciencefix to observe the breaking down of water into its components, hydrogen and oxygen, by passing an electric current through it.
06. ENERGY CHANGES
The formation of a mixture does not involve any change in energy, whereas the formation of a compound always results in the absorption or release of energy.
For example, during the formation of an aqueous sugar solution, no release or absorption of energy takes place. Whereas, water forms during the combustion of hydrogen gas in the presence of oxygen, which results in the release of a huge amount of energy.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MIXTURE AND COMPOUND IN TABULAR FORM
WHY IS WATER A COMPOUND AND AIR A MIXTURE?
Earlier, water and air were thought to be elements. However, it was later proven that water is a compound, whereas air is a mixture. Below is a list of evidence supporting this fact:
- Water is a compound because hydrogen and oxygen in water are chemically combined in a fixed ratio of 1:8 by mass. In contrast, the main components of air—nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor—are not chemically combined, making air a mixture.
- The chemical composition of water remains constant regardless of its source, whereas the composition of air varies from place to place. For example, during the rainy season, air becomes humid due to increased water vapor. Additionally, impurities such as sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide can alter the composition of air in certain locations.
- Water exhibits properties entirely different from its constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen. For example, the oxygen in water does not support combustion. In contrast, air is a mixture because its components retain their individual properties. For instance, the oxygen in the air supports combustion.
- Energy changes occur during the formation of a compound, as seen in the formation of water. When you ignite a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen, it releases a significant amount of energy to form water. However, mixing the components of air does not cause any energy change, further proving that air is a mixture.
The chemical formula of water is fixed as H₂O, whereas the variable composition of air prevents it from being represented by a single chemical formula.

Why is water a compound and air a mixture?