Difference Between Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids
Metals vs Nonmetals vs Metalloids: Key Differences, Properties & Examples | Selftution.com
Struggling to understand metals, nonmetals, and metalloids? Selftution.com – the #1 trusted educational website – breaks down their differences with clear comparisons, charts, and real-world applications. Master chemistry the easy way!
In the earlier post, Elements and Compounds, we learned that scientists have discovered a total of 118 elements so far. Among them, 94 elements are metals, 17 are nonmetals, and the remaining 7 elements are metalloids.
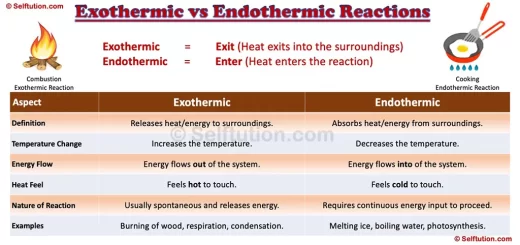
- Metals are generally shiny, good conductors of electricity, and malleable.
- Nonmetals tend to be dull, poor conductors, and brittle.
- Metalloids have properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
Understanding the Difference Between Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids is essential to grasping how elements behave in nature and their various uses.
Metalloids, for example, exhibit characteristics of both metals and nonmetals, making them unique in their properties.
In this blog, we will explore how these three categories differ in terms of physical and chemical properties, along with their practical applications in daily life.

The above demarcation between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids may vary since the nature of some elements is still under research.
Metals
Metals are hard, opaque, lustrous materials that are good conductors of heat and electricity. They are malleable and ductile, can withstand longitudinal pull, and produce a resonant sound when struck. They form basic oxides on reacting with the air and evolve hydrogen on reaction with water and dilute acids. Click here to know more about the physical and chemical properties of metal.
Nonmetals
Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electricity and are non-malleable and non-ductile. They do not exhibit luster and do not produce resonant sounds when struck. Nonmetals form acidic oxides when reacted with oxygen and do not evolve hydrogen when reacted with dilute acids. They are further divided into halogens and noble gases.
- Halogens: We derive the word halogen from ‘hal‘, which means salt, and ‘gen,’ which means generation. Thus, halogens are salt producers, as they react with metals to form a range of salts. For example, NaCl, KBr, etc.
- Noble gases: These are 6 monoatomic gases, i.e., He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn. They are chemically inert and almost inactive. Due to its inactive nature, we use argon in light bulbs to prevent the tungsten filament from oxidizing.
Click here to learn more about the physical and chemical properties of metal
Metalloids
Metalloids are those elements that show properties of both metals and nonmetals. They have physical and chemical properties intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Commonly recognized metalloids are Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), and Tellurium (Te). The less commonly recognized metalloid is Polonium (Po). Some of the uses of metalloids are :
- Boron: used as an insecticide and in fire retardants.
- Silicon: Silicon gel is applied to burn patients to absorb moisture. Silicon, being a semiconductor of electricity, is extensively used for the manufacture of transistors in the electronics industry.
- Arsenic: It finds use for medicinal purposes.
- Antimony: Used as an antiparasitic drug.
- Germanium finds application along with silicon in cell phones as a semiconductor.
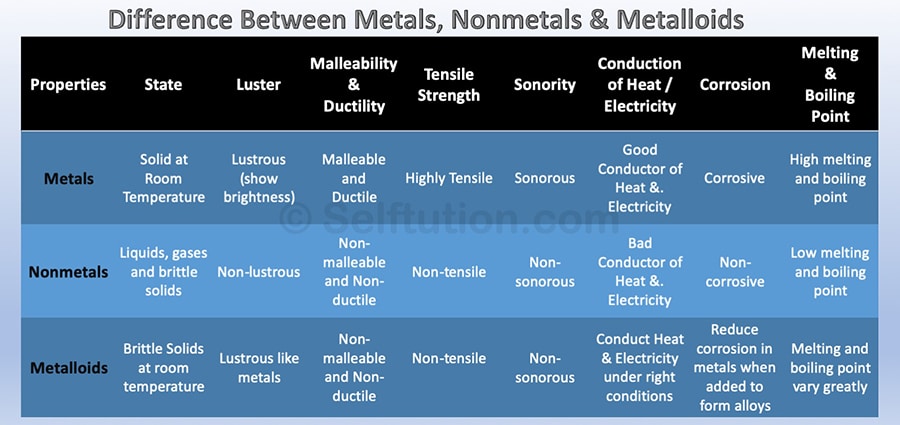
The difference in physical properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
The difference in Properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
- State: Metals and metalloids are generally solid at room temperature, whereas nonmetals exist as liquids, gases, or brittle solids. Metalloids are brittle solids that crumble to powder when struck.
- Luster: Metals are lustrous, i.e., show brightness, whereas nonmetals are non-lustrous. Metalloids exhibit metallic luster and may look like metals.
- Nature: Most metals are malleable and ductile, except zinc and mercury. Nonmetals are mostly non-malleable and non-ductile. All metalloids are brittle solids; therefore, they are not used for structural purposes. For example, Silicon is a brittle solid, but it is lustrous and acts as a good conductor of electricity under certain conditions.
- Tensile Strength: Metals have high tensile strength; therefore, they are extensively used for structural purposes. Whereas, nonmetals and metalloids have poor or low tensile strength. However, as an exception, carbon fibers made out of carbon, a nonmetal, have very high tensile strength.
- Conduction of Heat/Electricity: Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity, whereas nonmetals are non or poor conductors. Metalloids are semiconductors of electricity and show average transmission of heat under certain temperature conditions.
- Chemical properties: Metals lose or donate valence electrons and form cations, whereas nonmetals gain or accept electrons to form anions. Thus, metals and nonmetals combine through the ionic bond to form a compound. However, nonmetals also share electrons to form a compound through the covalent bond. Chemically, metalloids behave mostly as nonmetals. However, they can combine with metals to form an alloy.
You may also like…... Types of Chemical Reactions in Chemistry