Types of Motion in Physics with Examples
When an object’s position changes with time, we say it is in motion.
Different objects have different types of motion. For example, a train moves straight along its track, a fan rotates around its axis, and the Earth revolves around the sun. There can be many more such examples.
We can classify these different types of motion based on a path, periodicity, and an object’s speed.
- Based on the path followed by an object, there are five types of motion: translatory, rotatory, circular, oscillatory, and vibratory motion.
- Based on the periodicity, there are two types of motion: periodic and non-periodic motion.
- Finally, based on speed, there are two types of motion: uniform and non-uniform motion.
Topics Covered
Types of Motion Based on Path
As mentioned earlier, there are five types of motion based on the path: translatory, rotatory, circular, oscillatory, and vibratory motion.
01. TRANSLATORY MOTION
If an object moves in a line in such a way that every point of the object moves through the same distance in the same time, then the motion of the object is called translatory motion.
Let us consider this example:
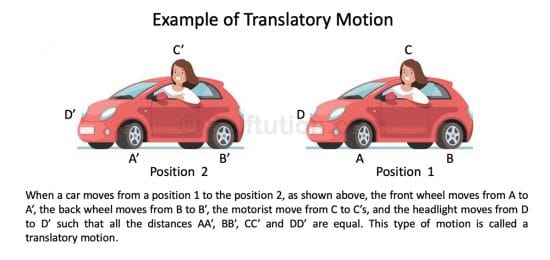
Translatory Motion with Example
Some other examples of translatory motion are:
- An apple falling from a tree,
- A boy walking on a road,
- The motion of a box when pushed from one corner of the room to the other, etc.
Translatory motion can be further of two types:
- Rectilinear or linear motion, and
- Curvilinear motion.
A. Rectilinear or linear motion
If the translatory motion of a body is along a straight line, it is said to be the rectilinear or linear motion.
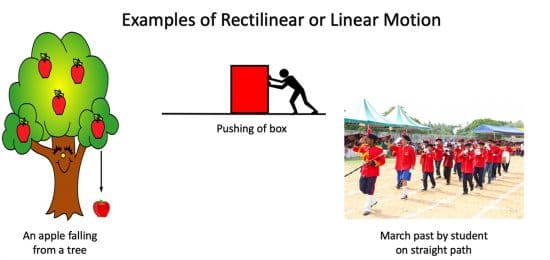
Types of rectilinear or linear translatory motion with examples
Some other examples of rectilinear or linear motion are:
- A stone falling straight toward the surface of the Earth,
- A car moving on a straight road,
- The motion of the bullet fired from the gun, etc.
A. Curvilinear motion
If the translatory motion of a body is along a curved path, it is said to be curvilinear motion.
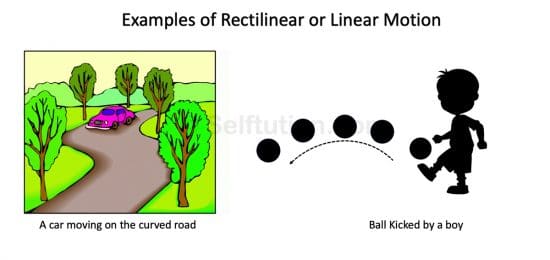
Types of Curvilinear Motion with examples. Clipart Courtesy http://clipart-library.com/
Types of curvilinear motion with examples – a car moving on a curved road and a ball kicked by a boy.
Some other examples of curvilinear motion are:
- The motion of the cycle while taking a turn on the road,
- The revolution of the Earth around the Sun.
- A path followed by a javelin thrown by an athlete, etc.
02. ROTATORY MOTION
If an object moves in such a way that every point of the object moves about a fixed axis, then the motion of the object is called rotatory motion.
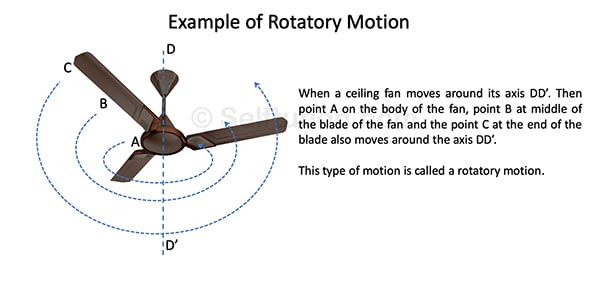
Explanation of rotatory motion with an example
Some other examples of rotatory motion are:
- The spinning of a top on its axis.
- The rotation of the Earth on its axis.
Difference between Rotatory and Translatory Motion – A rotatory motion is different from a translatory motion because, in rotatory motion, different parts of the object move through different distances at the same time. The body’s part near the rotation axis travels a smaller distance than the distant parts of the body.
03. CIRCULAR MOTION
The motion of the body along a circular path is called circular motion. Circular motion is a special type of curvilinear motion in which the distance of a moving object from a fixed point (called the center) does not change.

Example of circulatory Motion – The motion of a satellite around the Earth.
Some examples of circulatory motion are:
- A girl whirling a stone tied at the end of a string.
- The movement of the hands of a clock.
- Merry-go-round.
- Bicycle wheel.
- An athlete running on a circular track,
- The motion of the blades of the fan, etc.
Most of the examples of circular motion are the same as those of rotatory motion. So, let’s understand the difference between circular and rotatory motion.
Difference between Circular, Rotatory, and Curvilinear Motion –
- In rotatory motion, the axis of rotation passes from a point in the body itself, whereas in a circular motion, it passes through a point outside the body.
- In circular and rotatory motion, the distance of a point of the body from a fixed point always remains the same, whereas it is not the same in curvilinear motion.
04. OSCILLATORY MOTION
To and fro motion of a body from its rest position (or mean position) is called oscillatory motion. For example, the motion of a swing and the motion of the pendulum of the wall clock represent the oscillatory motion.
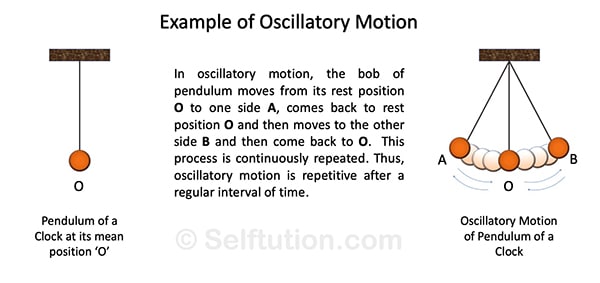
Explanation of Oscillatory Motion with an example
Explanation of Oscillatory motion with an example. Some other oscillatory motion examples are the movement of a spring, the motion of a swing, etc.
05. VIBRATORY MOTION
The vibratory motion is a type of oscillatory motion with a slight difference. In vibratory motion, a part of the body always remains fixed and the rest part moves to and fro about its mean position. During vibratory motion, the shape and size of the object change.
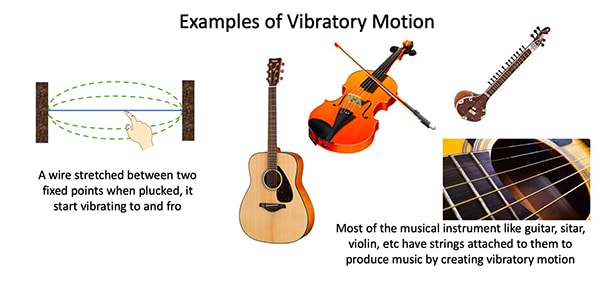
Various types of musical instruments that create vibratory motion
Examples of various types of instruments creating vibratory motion, ranging from a wire simply stretched between two fixed points to the sitar, guitar, violin, etc
Some other examples of circulatory motion are:
- The motion of our chest during breathing.
- The motion of the tuning fork when hit with a rubber pad.
Back to the types of motion based on the path
Types of Motion Based on Periodicity
As brought out earlier, there are two types of motion, based on periodicity. These are periodic and non-periodic motions.
01. PERIODIC MOTION
The periodic motion is the type of motion that gets repeated after a regular interval of time.
Some periodic motion examples are:
- The Earth completes one round around the sun in 356-1/4 days, and this motion gets repeated after every 356-1/4 days. Thus, it is a periodic motion.
- The moon revolves around the Earth, completes one revolution in 27 days, and then repeats its motion.
- The pendulum of the clock repeats its motion every 2 seconds.
- The motion of the needle of a sewing machine.

It will be interesting for you to know that circular and oscillatory motion is repetitive. Therefore, they come under the category of periodic motion.
02. NON-PERIODIC MOTION
The non-periodic motion is the type of motion that does not repeat itself after a regular interval of time.
For example,
- The motion of a footballer during a match.
- A ball rolling down the ground gradually slows down and finally stops,
- The motion of sea waves, etc.
Back to the types of motion based on the path
Types of Motion Based on Speed
As brought out earlier, there are two types of motion, based on Speed. These are uniform and non-uniform motions.
01. UNIFORM MOTION
If a moving body travels an equal distance in an equal interval of time, its motion is said to be uniform. Thus, for uniform motion, the speed of the moving body remains constant. Let us understand this by an example,
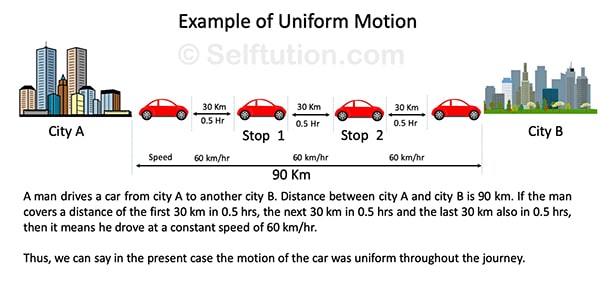
Explanation of Uniform Motion with an example
Some other examples of uniform motion are:
- The revolution of the Earth around the Sun.
- The revolution of the moon around the Earth.
- The movement of the hands of a clock.
02. NON-UNIFORM MOTION
If a moving body travels an unequal distance in an equal interval of time or an equal distance in unequal time intervals, its motion is said to be non-uniform. Thus, for the non-uniform motion, the speed of the moving body does not remain constant. Let us understand this by an example,
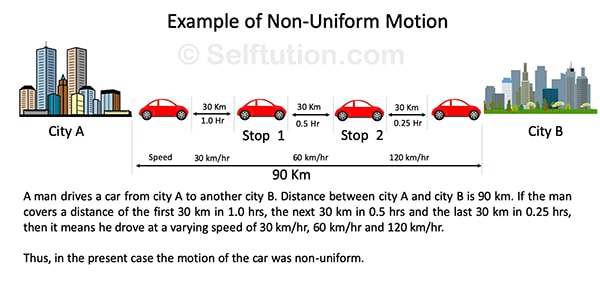
Example of Non-Uniform Motion
Back to the types of motion based on the path
For more such information, please visit are YouTube channel SELFTUTION