Difference between Simple and Complex Permanent Tissue
The permanent plant tissue forms the bulk of the plant body. Unlike, meristematic tissues, these tissues do not divide. They take a permanent shape and become specialized to perform a specific function for the rest of their life. Based on the number and kind of cells involved in the formation of tissue, permanent tissues are of two types – simple permanent tissues and complex permanent tissues. Simple permanent tissue provides support and protection to the plant, whereas complex permanent tissue helps in the conduction of nutrients and water.
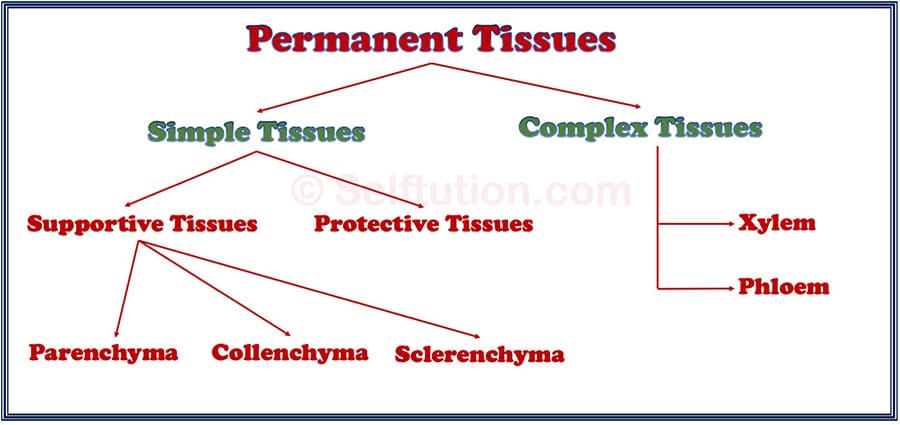
Types of Permanent Tissues
New cells form when the meristematic plant tissues divide. These newly formed cells elongate, mature, and get differentiated into various types of permanent tissues. Permanent plant tissues do not divide further. Permanent plant tissue is the group of cells in which growth has either stopped completely or for the time being.
SIMPLE PERMANENT TISSUES
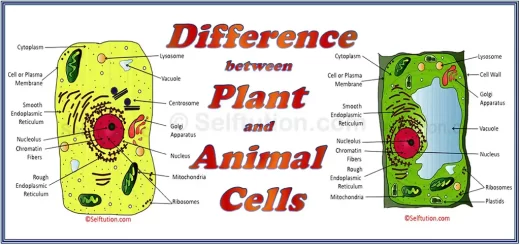
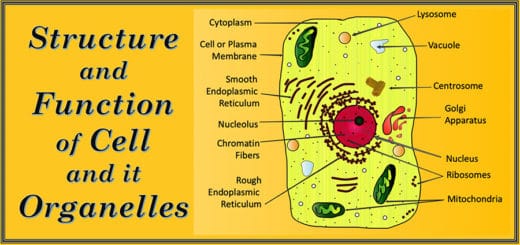
Simple permanent tissues are virtually present in every part of the plant. They consist of only one type of cell. All cells that make up the simple permanent tissue are similar in structure and perform the same function. The major functions of the simple permanent tissue are to provide support and protection to the plant. Apart from these, they are also responsible for: tissue repair, secretion, food storage, and photosynthesis.
According to the function performed simple permanent plant tissues are of two types:
- Protective Tissues, and
- Supportive Tissues.
Protective Plant Tissues
These tissues consist of cells with thick walls. They are living cells present on the surface of leaves, roots, and stems. For example,
- The epidermis of leaves, which secretes a waxy waterproof substance, and
- Cork cells in the barks contain another strong waterproof material.
Supportive Tissues
As the name suggests, the main function of the supporting tissues is to provide support to various parts of a plant. They may consist of living or dead cells. Based on varying cell properties supportive simple permanent tissues are of several types. The three most important ones are – parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma and collenchyma consist of living cells, whereas sclerenchyma is made up of cells that have become dead. Parenchyma mainly acts as a packing tissue. They provide mechanical strength and also store food. Collenchyma tissue provides flexibility as well as mechanical support to plants. Last but not least, sclerenchyma provides rigidity to the plant body.
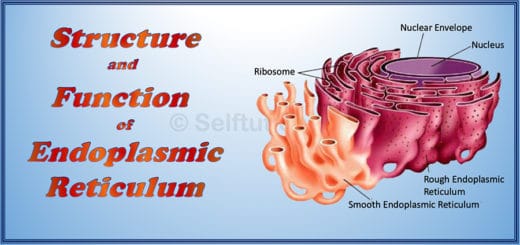
COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUES
Complex permanent plant tissues are present in the vascular region of the plant. They help in the conduction of nutrients and water throughout the plant body. Complex permanent plant tissue consists of a group of multiple types of cells that have a common origin but perform different functions. It consists of both living and dead cells which coordinate together to perform the same specialized functions in the plant body. Based on their structure and function performed, complex permanent tissues are of two types – xylem and phloem.
Xylem
The xylem tissue is responsible for the conduction of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and stems. It also provides support to the plants. It has four elements. They are tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibers.
Phloem
This complex permanent tissue helps in the conduction of food that is prepared by photosynthesis in the leaves to various parts of the plant. Phloem consists of four elements. They are sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SIMPLE AND COMPLEX PERMANENT TISSUES
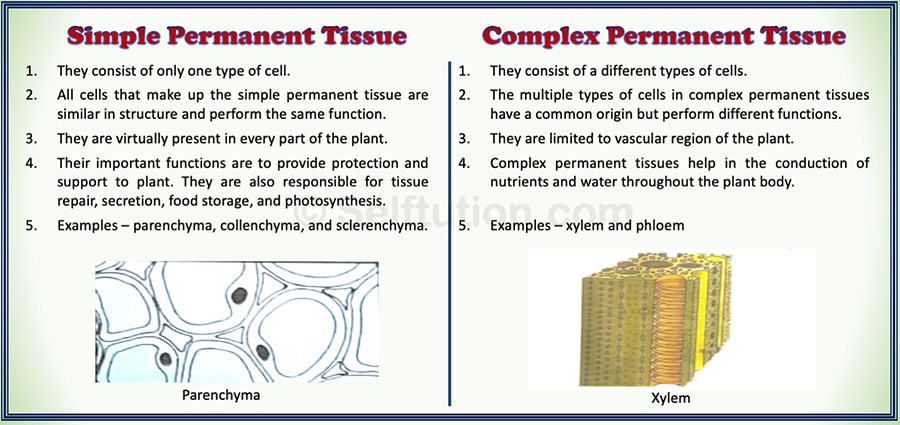
Difference between Simple and Complex Permanent Plant Tissue
For more such photos, please visit capturing moment@shutterstock
For instant discounts click here