Natural Disasters | Types, Examples & Precautions
Natural Disasters – Types, Causes, Examples & Safety Precautions | Selftution.com
Learn about earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and more with detailed guides. Discover how to stay safe before, during, and after disasters. Selftution.com is the best educational website for clear, reliable, and practical learning.
Introduction to Natural Disasters
Natural disasters are sudden, destructive events caused by natural forces. They can lead to significant loss of life and property, along with long-term socio-economic impacts.
We define a disaster as any event that disrupts normal life and damages communities. While disasters can be human-made, this blog will focus on natural calamities that strike with little warning, often devastating entire regions.
Here we will explore various types of natural disasters, including earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and more. Additionally, we’ll provide real-life examples and outline precautions to minimize risks and protect ourselves when nature turns unpredictable.
Topics Covered:
- Earthquakes: their effects and precautions
- Floods: their effects and precautions
- Drought and its prevention
- Cyclones’ effects and precautions
- Volcanic Eruptions: their effects and precautions
- Tsunami and precautions
Refer to the image below for various types of natural disasters –

Types of Natural Disasters
NATURAL DISASTERS
Nature, in all its generosity, provides us with countless gifts—beauty, resources, and sustenance. Yet, it is also nature that, on occasion, unleashes its fury in the form of natural disasters.
Natural disasters are devastating events triggered by Earth’s natural processes. Some examples of natural disasters are – earthquakes, floods, droughts, cyclones, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
When such disasters strike, they often lead to immense loss of life, destruction of property, and disruption of communities.”
EARTHQUAKES
Earthquakes are sudden shaking or vibrations of the Earth’s surface. They happen because of sudden movements deep inside the Earth. The strongest vibrations are felt at the epicenter, which is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above where the earthquake starts. The starting point, deep underground, is called the focus. Earthquakes are mainly caused by the movement of tectonic plates or molten rocks beneath the Earth’s crust. Sometimes, volcanic eruptions can also trigger earthquakes.
 Video courtesy: Frank Gregario @ YouTube
Video courtesy: Frank Gregario @ YouTube
Seismology is the science that studies earthquakes and tries to predict them. We measure the strength of an earthquake using the Richter Scale, which ranges from 1 to 10. A reading of ‘1’ shows very small vibrations, while a reading closer to ’10’ indicates a much stronger earthquake. Small earthquakes with an intensity of 1-2 happen often, but we usually don’t feel them. However, an earthquake with a reading of 5 or above can cause serious damage. The device used to measure the strength and duration of an earthquake is called a seismograph.

Seismograph. Image courtesy Wikipedia
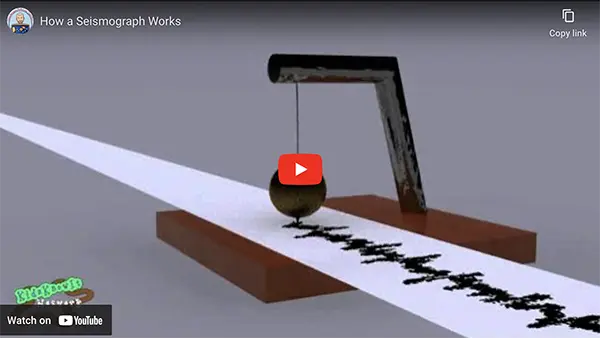 How a seismograph works. Video courtesy: KidsKnowit @youtube
How a seismograph works. Video courtesy: KidsKnowit @youtube
Effects of Earthquakes:

We cannot predict natural disasters like earthquakes. It can occur at any time. Due to earthquakes, buildings get damaged and collapse, and people die when they get stuck in the ruins. Roads get cracked, flyovers collapse, and railway lines get twisted, resulting in transport disruption. Electricity poles break, and wires get dislocated. In coastal areas, earthquakes cause tsunamis and floods. Also, landslides occur in the mountainous regions due to the vibration of the Earth.
Precautions for Earthquakes
We know that it is difficult to predict natural disasters like earthquakes. But whenever you feel an earthquake, take the following precautions to minimize risks:
- Build earthquake-proof houses and buildings.
- Run out of the building immediately to an open area where nothing can fall on you.
- If you are unable to run out, then you should move under heavy furniture such as beds and tables.
- Keep yourself away from buildings, trees, and electric poles, which can collapse and cause injury.
- Avoid using lifts. Use the staircase.
- Conduct mock drills in schools, offices, and residential complexes to spread awareness about the precautionary measures.
Top 10 Deadliest Earthquakes in History:
- Shaanxi, China, January 23, 1556, Richter Scale – 8, more than 830,000 people died.
- Port-au-Prince, Haiti, January 12, 2010, Richter Scale – 7.0, estimated deaths 316,000.
- Tangshan, China, July 27, 1976, Richter Scale – 7.5, more than 255,000 deaths.
- Antakya, Turkey, May 21, 526, Richter Scale – do not exist, more than 250,000 deaths.
- Aleppo, Syria, August 9, 1138, Richter Scale – do not exist, more than 230,000 people died.
- Sumatra, Indonesia, December 26, 2004, Richter Scale – 9.1, nearly 227,000 deaths.
- Damghan, Iran, December 22, 856, the Richter Scale – does not exist, more than 200,000 people died.
- Haiyuan, China, December 16, 1920, Richter Scale – 7.8, about 200,000 deaths.
- Ardabil, Iran, March 23, 893, Richter Scale – do not exist, more than 150,000 people died.
- Kanto, Japan, September 1, 1923, Richter Scale – 7.9, about 149,000 deaths.
The top 10 deadliest natural disasters from floods in World History
FLOODS – Most Commonly Occurring Natural Disaster
Floods, a common natural disaster, occur when excessive rainfall causes rivers to overflow, raising water levels beyond their banks and submerging nearby areas. However, heavy rainfall isn’t the only cause of flooding. Other factors include:
- The melting of glacier snow in the mountains during the summer months.
- Cyclones, storms, and tsunamis, especially common in coastal regions.
- Silting of riverbeds or blockages in river channels caused by landslides.

Houses on the outskirts of Lumberton, North Carolina, sit in floodwater caused by Hurricane Florence on September 17, 2018. Image courtesy Business Insider
When there is sudden flooding of water due to a cloud burst or heavy rain, we call it a flash flood. A natural disaster like this occurred in Leh, Ladakh, India, in 2010, causing heavy damage.
Effects of Floods
Apart from rendering people homeless, there are many other effects of floods:
- Crops get washed away by strong water currents.
- The submergence of roads and railways affects transport and communication.
- People face a loss of livestock and a shortage of food and drinking water.
- An outbreak of diseases like cholera, diarrhea, malaria, and dengue occurs in flood-hit areas
Precautions for Floods
To face natural disasters like a flood, take the following precautions:
- Be alert and pay attention to the warnings in the newspapers, radio, and on television.
- A rise in the river water level should be closely monitored.
- Keep ready a good stock of food, drinking water, and essential medicines.
- Be prepared to move to higher ground.
- Try to drink boiled water only.
- The use of electrical appliances should be avoided if floodwater enters the house.
Ways to Control Floods

- To prevent natural disasters like floods, more trees should be planted. Trees help in preventing water from spreading fast, thus controlling floods.
- Dams should be built over rivers to slow down the flow of water.
Top 10 Deadliest Floods in History:
- China Flood, July 1931, Rivers – Yangtze, Yellow River, and Huai, 1 million to 4 million people died.
- Yellow River Flood, China, September 1887, River – Yellow River, 900,000 to 2 million deaths.
- Yellow River Flood, China, June 1938, more than 800,000 deaths. It was artificially created by the Chinese government during the Sino-Japanese War.
- Typhoon Nina, China, August 1975, River – Ru River, flood instantly killed 86,000 people, and 145,000 died due to starvation and diseases.
- Yangtze River Flood, China, 1935, nearly 145,000 killed.
- St Felix’s Flood, The Netherlands, November 1530, Storm flood, an estimated 120,000 people were killed.
- Red River Delta Flood, North Vietnam, June to October 1971, Rivers – Thao, Lo, and Da, nearly 100,000 people lost their lives.
- Jiangsu-Anhui Flood, China, May 1911, Rivers – Yangtze and Huai, 100,000 deaths.
- St. Lucia Flood, The Netherlands, December 1287, Storm flood, nearly 80,000 people lost their lives.
- North Sea Flood, The Netherlands, June 1212, Rivers – Rhine, Scheldt, and the Meuse, claimed 60,000 lives.
DROUGHT
It’s a peculiar contrast of nature that while some regions experience heavy rainfall and flooding, others receive little to no rain, leading to drought. A drought is a natural disaster where an area suffers from prolonged periods of inadequate rainfall. This results in rivers and underground water sources drying up, making it difficult for farmers to grow crops and for livestock to survive due to the scarcity of water.
Droughts not only impact agriculture but also lead to severe water shortages for daily human needs. In extreme cases, prolonged droughts can lead to famine, where there is a widespread shortage of food, causing immense suffering and loss of life. Livelihoods are devastated, and the entire ecosystem is disrupted as people, plants, and animals struggle to survive.
Globally, many regions, especially those already prone to arid conditions, face severe droughts, leading to economic and environmental crises.

The carcasses of cattle died due to a lack of water
Prevention from Droughts
Natural disasters like droughts can be prevented if we adopt the following methods:
- Implement proper rainwater harvesting systems in drought-prone areas.
- Plant trees in huge numbers.
- Grow drought-resistant crops like millet, maize, etc.
- Adopt better techniques for irrigation, and
- Build dams to store excess water in reservoirs.
CYCLONES
Cyclones are powerful, rotating wind systems that form around a low-pressure center, typically over warm ocean waters. They develop when warm, moist air rises from the surface of the ocean, creating a void that is filled by cooler air from the surrounding areas. As this process continues, the rising air begins to rotate due to the Earth’s rotation, leading to the formation of a cyclone.
For a storm to be classified as a cyclone, wind speeds must exceed 100 km/h, but cyclones can intensify with wind speeds reaching up to 300 km/h in the most severe cases. The warm ocean waters fuel these storms, making coastal regions particularly vulnerable to their destructive power. Cyclones bring with them not only high-speed winds but also torrential rainfall and storm surges, which can lead to devastating flooding and widespread destruction of property.

Effect of Cyclones
Cyclones are among the most feared natural disasters, alongside earthquakes and floods, because of their capacity to cause mass devastation. Entire communities can be uprooted, agricultural lands flooded, and infrastructure destroyed. In addition to the physical destruction, the aftermath often includes loss of life, displacement of populations, and long-term economic challenges for the affected regions.
Modern meteorology has made it possible to predict cyclones more accurately, but their destructive impact remains a major global concern, particularly in tropical and coastal areas.
Precautions from Cyclones
Nowadays, with the advent of good technology, predicting natural disasters like cyclones has become easier. Thus, whenever authorities raise a warning, we should take the following measures:
- Be alert and attentive to the warnings and weather forecasts through radio, newspaper, and television.
- Be ready to move to a safer place.
- Store food well in advance.
- Store essential medicines and prepare a first-aid kit.
- Avoid going near or into the sea.
Top 10 Deadliest Cyclones in History:
- Great Bhola Cyclone, Bangladesh, November 1970, the death toll was 300,000 to 500,0000.
- Hoogly River Cyclone, India & Bangladesh, 1737, 300,000 to 350,000 people lost their lives.
- Haiphong Cyclone, Vietnam, October 1881, more than 300,000 deaths.
- Coringa Cyclone, India, November 1839, killed 300,000 people and destroyed 20,000 ships.
- Backerganj Cyclone, Bangladesh, 1584, the estimated death toll was 200,000.
- Great Backerganj Cyclone, Bangladesh, October 1876, more than 200,000 deaths.
- Chittagong Cyclone, Bangladesh, 1897, killed 175,000 people.
- Cyclone 02B, Bangladesh, April 1991, killed more than 135,000 people and rendered 10 million people homeless.
- Cyclone Nargis, Myanmar, May 2008, the death toll was 84,500, and 53,800 were missing.
- Bangladesh Cyclone of 1942, Bangladesh, October 1942, more than 61,000 people lost their lives.
VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS – VERY COMMON NATURAL DISASTERS
A Volcano is an opening on the earth’s surface through which Magma (hot molten rock) comes out.
When magma builds up beneath the Earth’s crust, it forces its way out to the surface. The opening on the surface through which magma flows out is called a Vent. This phenomenon is called a volcanic eruption. When the magma flows out of the vent, it is called Lava. Along with lava. Hot gases and ashes come out. As the lava cools down gradually, it forms a Volcanic mountain. A bowl-shaped hollow is formed at the top, which is called the Crater.
There are three types of volcanoes:

Active Volcano – Mt. Stromboli, Italy
Active Volcanoes are the most dangerous ones. These volcanoes have erupted recently and can erupt again, for example,
- Pacaya, Guatemala
- Mt. Stromboli, Italy
- Sakurajima, Japan

Mt. Kilimanjaro in Tanzania.
Dormant Volcanoes: They have erupted in the past and have not erupted for many years. But they have chances of erupting again. We also call them ‘sleeping volcanoes’. For example,
- Mt. Kilimanjaro in Tanzania.
- Mt. Vesuvius in Naples, Italy, which was considered extinct, erupted recently.

Chimborazo in Ecuador
Dead or Extinct Volcanoes: They have not erupted for thousands of years. For example
- Mount Kulal in Kenya,
- Chimborazo in Ecuador
We mostly find volcanic areas along the Pacific Ocean. It is called the Ring of Fire.
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
Natural disasters like volcanic eruptions can result in earthquakes in nearby areas. They destroy their surroundings by spreading lava over large areas, resulting in the burying of farmlands, forests, residential areas, and transport lines. Ash and poisonous gases that erupt cause air pollution and health hazards. Moreover, it disrupts air traffic, and aerial animals may lose their lives.
Precautions from Volcanic Eruptions
In the case of natural disasters like a volcanic eruption, we must take the following precautions
- Prepare ourselves to move to a safer place.
- Store food and water.
- Stay away from molten lava and hot gases
- Be attentive to the warnings and the announcements made by the authorities
TSUNAMI – A Rare Natural Disaster
A tsunami is a series of massive ocean waves triggered by underwater disturbances such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides. These disturbances displace large volumes of water, sending powerful waves across the ocean at speeds that can exceed 800 km/h. Unlike regular ocean waves, tsunami waves are much longer and can travel across entire ocean basins, making them a significant threat even far from their point of origin.
Tsunamis are unpredictable and can occur at any time, with little to no warning, especially in coastal areas. As these waves approach shallow waters near the shore, they grow in height dramatically, sometimes reaching up to 30 meters or more. This sudden surge of water can flood coastal regions, causing widespread destruction to infrastructure, homes, and agriculture. The force of the waves can sweep away buildings, vehicles, and anything in their path, leading to immense loss of life and property.

Tsunami – Sumatra, Indonesia
The effects of a tsunami are devastating, often compounded by the fact that it strikes with little warning, leaving people little time to evacuate. In addition to the immediate destruction, tsunamis can lead to long-term impacts such as contamination of freshwater supplies, disruption of livelihoods, and the displacement of large populations. Coastal regions in tsunami-prone areas are often equipped with early warning systems, but the sheer power of these waves makes them one of the most dangerous natural disasters on Earth.
On 26 December 2004, a severe tsunami that originated from Sumatra in Indonesia hit several countries in South-East Asia, killing nearly 3,00,000 people. It left many people homeless. It was perhaps the biggest natural disaster ever. Recently, an undersea earthquake and tsunami in Japan in 2011 destroyed over 2,00,000 houses, and more than 20,000 people died.
 Precautions from Tsunami
Precautions from Tsunami
To face natural disasters like a tsunami, take the following precautions:
- Install a good Tsunami Warning System to warn people well in advance.
- People living near the sea or a low-lying coastal region should immediately move to higher ground and stay there till it is safe to return.
Natural disasters can occur anywhere, anytime. They affect thousands of people at any single occurrence. The major task that follows any natural disaster is relief work. It is our basic duty to help in all possible ways. There are many government agencies and non-government organizations like the Red Cross Society, the World Health Organization, and UNICEF that provide help to people in different ways during any such natural disaster.

 Precautions from Tsunami
Precautions from Tsunami