Difference between Potential and Kinetic Energy | Examples
Mechanical Energy is the driving force behind every activity. In the world of physics, mechanical energy is categorized into two fascinating forms: potential and kinetic energy.
The difference between potential and kinetic energy lies in their nature. Kinetic energy arises from motion, while potential energy is the stored energy of a body at rest or in position.
At any given time, the total mechanical energy of an object equals the sum of its kinetic and potential energy. These concepts are fundamental to understanding energy transfer.
In this blog, we’ll define these energy types, explore their differences, and discuss real-life examples to make these concepts easy to grasp.
Skip to >>Five differences between potential and kinetic energy
DEFINITIONS
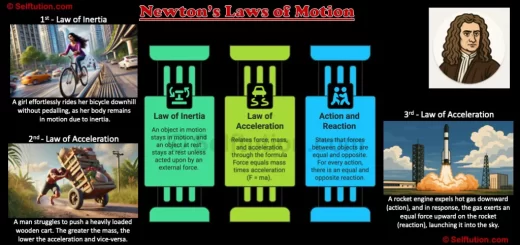
Definition of Mechanical Energy
Mechanical energy is the energy possessed by a body due to its state of rest or state of motion.
Definition of Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
The kinetic energy is the form of energy possessed by a body due to the virtue of its state of motion.
The potential energy is the stored up energy of a body due to the virtue of its state of rest or position which has the ability to do work.
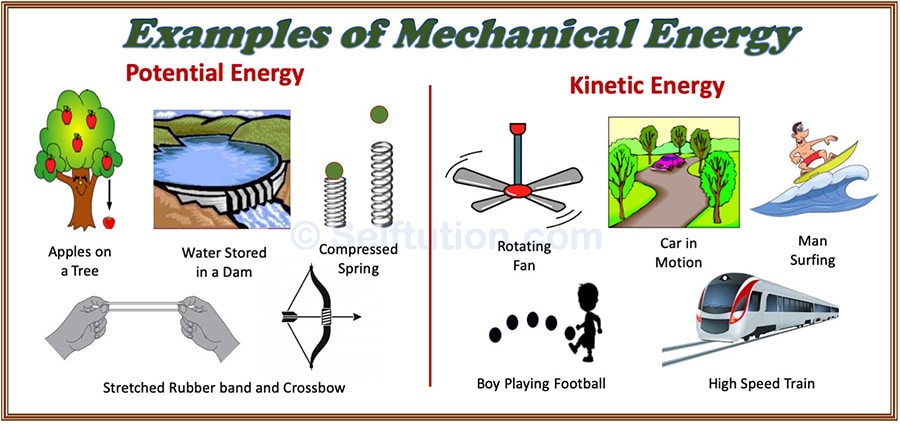
Examples of Mechanical energy – Potential and Kinetic energy
KINETIC ENERGY WITH EXAMPLES
The word kinetic comes from the Greek word ‘kinesis‘, which means ‘motion’. Thus, the form of mechanical energy possessed by all moving bodies is called motional or kinetic energy. Some examples of kinetic energy are-
- A fast-moving stone thrown toward a glass window can break a window pane when it strikes the pane. Thus, the stone in motion has kinetic energy.
- A hammer in motion, when it strikes a nail fixed in a wooden block, moves it further down into the block. Thus, the moving hammer possesses kinetic energy, which works on the nail to drive it further into the block.
- Some more examples of kinetic energy are – a bullet fired from a gun, a rolling ball, flowing water, moving air, a boy playing football, a swinging pendulum, the wind blowing, a flying bird, a train or car in motion, etc.
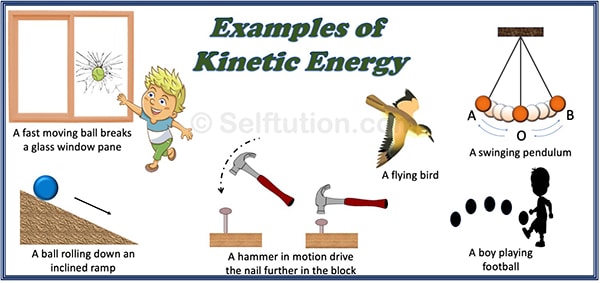
Examples of kinetic energy
Factors affecting the Kinetic Energy of a moving body
The kinetic energy of a moving body depends on the following two factors:
- The mass of the body: The greater the mass of the body, the higher its kinetic energy.
- The speed of the body: The greater the speed of the body, the higher its kinetic energy.
Expression of Kinetic Energy
If a body of mass ‘m‘ is moving with a speed ‘v‘, its kinetic energy is:
K.E. = 1/2 mv2
S.I. unit of kinetic energy is the Joule (J).
POTENTIAL ENERGY WITH EXAMPLES
“Potential” is a Latin word that means ‘to be able”. Therefore, the stored energy of a body due to the virtue of its state of rest or the position that can do work is called potential energy. The potential energy is of further two forms – gravitational and elastic. The gravitational potential energy is the energy possessed by a body due to a change in its position with respect to the Earth’s surface. Whereas, elastic potential energy is the energy stored in a body due to a change in shape and size of the object.
Like kinetic energy, the SI unit of potential energy is also Joule (J).
Gravitational Potential Energy with Examples
When we take a body from the earth’s surface to a height, work has to be done on the body against the force of gravity. This work gets stored in the body in the form of its potential energy. We call this gravitational potential energy. Some examples of gravitational potential energy are:
- A stone placed at a height has the gravitational potential energy stored in it. The stone has energy due to its position at a height. If we drop this stone on a nail fixed on a piece of board. It drives the nail into the board.
- Water stored in a dam has gravitational potential energy stored in it. When we allow this water to flow through the turbine, it produces electrical energy.

Examples of Gravitational Potential Energy
Factors affecting the Gravitational Potential Energy of a body
The gravitational potential energy of a body depends on the following two factors:
- The mass of the body: The greater the mass of the body, the higher its gravitational potential energy.
- The height of the body above the Earth’s surface: The greater the height of the body, the higher its gravitational potential energy.
Expression of Gravitational Potential Energy
If we move a body of mass ‘m‘ from the ground to a height of ‘h‘ above the Earth’s surface. The minimum force required to move the body will be the force of gravity on the body acting vertically downward. If ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity, then the force of gravity on mass ‘m‘ will be:
F = mg
Therefore, the work done on the body to rise to height ‘h’ is:
W = mgh
This work done against the force of gravity will get stored in the body in the form of its gravitational potential energy.
Thus, gravitational potential energy is:
P.E. = mgh
ELASTIC POTENTIAL ENERGY WITH EXAMPLES
To bring a change in the shape or size of an object, work needs to be done on the object. This work gets stored in the object in the form of its potential energy. We call this elastic potential energy. Some examples of elastic potential energy are:
- A wound-up watch spring has elastic potential energy because of the wound-up state of its coil. As the spring unwinds, it does work to move the arms of the watch.
- A compressed spring has elastic potential energy because of its compressed state. If we place a ball on the compressed spring and release the spring, the ball will fly away. Thus, the spring does work on the ball.
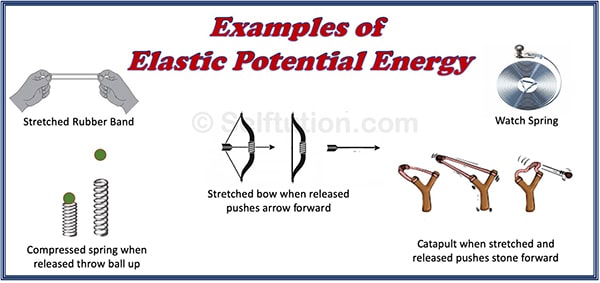
Examples of elastic Potential Energy
Expression of Elastic Potential Energy
If the length of a spring changes by ‘x’ due to the application of a force, then
P.E. = 1/2 Kx2
Here, K is an elastic constant or a force constant. Elasticity or the force constant is a property of an object (spring in the present case).
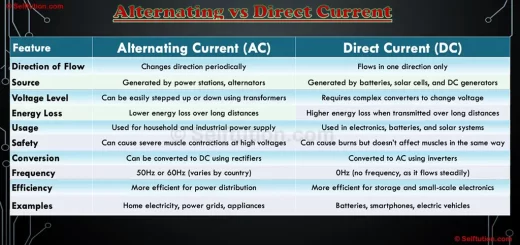
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY
- Potential energy is due to the state of rest, whereas kinetic energy is due to the state of motion.
- Factors affecting kinetic energy are the mass and speed of the body, whereas potential energy depends upon mass, change in height, and change in the shape of a body.
- Potential energy can only change to kinetic energy. Whereas kinetic energy can change into different forms of energy, like potential energy, heat energy, sound energy, light energy, etc.
- We can transfer kinetic energy from one body to another, but the same is not possible with potential energy.
- Kinetic energy is relative to the environment of a body, whereas potential energy does not depend on the environment of a body.

Difference Between Potential and Kinetic Energy in tabular form
You may also like…... Types of Chemical Reactions in Chemistry