Measurement for Kids | SI Units & Examples
Measurement for Kids | SI Units & Examples – Fun & Easy Learning!
Teach kids the basics of measurement and SI units with simple explanations, colorful diagrams, and real-world examples. Selftution.com is the best educational website for making science clear, engaging, and perfect for young learners!
Welcome to Selftution.com – where learning becomes fun and effortless! So, let’s begin.
Measurement is not only for kids; it’s something everyone needs to do in life.
Whether it’s tracking time, managing money, or keeping an eye on our health, measurements help us stay organized and make better decisions.
Teaching kids the basics of measurement not only prepares them for practical tasks but also helps them develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Every day, we encounter situations where we measure length, mass, time, and temperature. For example,
- When you try to find out the distance between your house and your friend’s house, you measure the length. This helps you plan your trip better and estimate how long it will take to get there.
- If you want to know the quantity of vegetables or grocery items you need to buy, you measure mass or weight. This ensures you buy the right amount, avoiding waste or shortages.
- When you try to determine how long it will take you to complete your homework, you measure time. This helps you manage your schedule and prioritize your tasks efficiently.
- When you want to know how cold or hot your milk is, you measure its temperature. This helps you ensure that it’s safe to drink and at a comfortable temperature.

Measuring the Weight of Vegetables
TOPICS COVERED:
IMPORTANCE OF MEASUREMENT FOR KIDS

Measuring Temperature using a thermometer
Measurement is essential for accuracy in our daily activities. Without it, we can’t correctly judge any object’s length, mass, time, or temperature. For instance, when you feel sick, your mother uses a thermometer to measure your body temperature. If the thermometer shows 100°F, she knows you have a fever because the normal body temperature is 98.6°F. This accurate measurement confirms you are unwell and need care.
Similarly, measurement helps us buy the right amount of groceries, ensuring we don’t buy too much or too little. It also lets us plan our schedules by determining how long tasks will take, helping us manage our time effectively. In cooking, measuring ingredients accurately ensures the food tastes good and is safe to eat. Measurement helps us understand weather conditions, allowing us to dress appropriately and plan our activities. Accurate measurement is crucial for making correct judgments and decisions in our everyday lives.
MEASUREMENT vs ESTIMATES
People often make guesses about various things. For example, we might estimate how far New York is from Chicago or how warm a room is. These estimates are guesses based on our knowledge and common sense. While estimates can be useful, they are not exact and can sometimes be wrong.

Basics of Measurement Kids
In contrast, measurements provide precise and accurate information. In physics and other fields, accuracy is crucial. For example, if we need to lay a railway line from New York to Chicago, every kilometer matters. Estimating the distance could result in a railway line that is either too short or too long, causing significant issues. Therefore, to avoid such mistakes, we need to carry out accurate measurements of the distance between the two cities.
In summary, while estimates are convenient and often helpful, they lack the precision required for many tasks. Accurate measurements ensure correctness and reliability, especially in critical projects like building infrastructure.
DEFINITION OF MEASUREMENT FOR KIDS
Measurement is a comparison of an unknown quantity with a known fixed quantity.
IMPORTANT TERMS RELATED TO MEASUREMENT
Before we can proceed further with the measurement of length, mass, time, and temperature, you need to understand the following terms:
A. PHYSICAL QUANTITY
A physical quantity is something that can be measured. Examples of physical quantities include length, time, mass, and volume. We can quantify these aspects of the physical world using various tools and units.
For instance, you cannot measure your friend’s level of love, anger, sincerity, or honesty. These qualities are subjective and cannot be quantified. However, you can measure your friend’s height, weight, and body temperature. In this example, emotions and traits like love and honesty are not physical quantities, while height, weight, and body temperature are physical quantities.
Physical quantities are essential in science and everyday life because they allow us to describe the world in precise and consistent terms. By measuring physical quantities, we can better understand, compare, and analyze different aspects of the physical world.
Physical quantities are of two types:
- Fundamental Physical Quantities: These quantities are the basic measurements from which other quantities are derived. Examples include length (measured in meters), time (measured in seconds), mass (measured in kilograms), and electric current (measured in amperes).
- Derived Physical Quantities: These quantities are those obtained from the fundamental quantities through mathematical relationships. Examples include speed, which is derived from length (distance) and time, and volume, which is derived from length (height, width, and depth). These quantities help describe more complex aspects of the physical world.
B. UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
When we compare the unknown quantity of things or substances with a known fixed quantity, we call it measurement. This fixed quantity with which we compare unknown quantities is called a unit of measurement. For example, when someone requests 5 glasses of water, then ‘a glass of water’ is a unit and the person is requesting 5 units of the same. Hence, to express the result of a measurement of a physical quantity, we must know the following:
- The unit in which the quantity is to be measured, and
- The numerical value that expresses how many times the above-mentioned unit is there in that given quantity.
Let us take one more example,
If the length of a piece of cloth is 10 meters, it means that we measure the length in the unit ‘meter’ and this unit is present 10 times in the length of that piece of cloth. Thus, a measurement consists of two parts – the magnitude (or number) and a unit.
Back to the Importance of Measurement for Kids
C. STANDARD UNITS OF MEASUREMENT FOR KIDS
In ancient times, various units were utilized for measurement across different countries, relying on practical methods like footsteps, arm-length, hand span, ropes, and sticks. The cubit, for instance, was a common unit, representing the length from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. Similarly, a hand span was determined from the tip of the thumb to the tip of the little finger when the hand was fully stretched. These units, rooted in human anatomy, facilitated everyday measurements but lacked standardization, leading to variations.
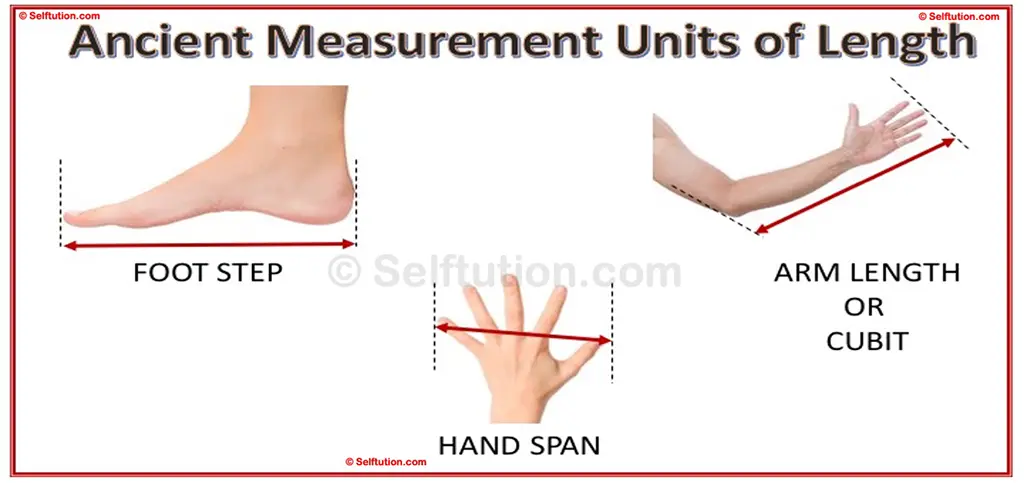
Ancient Measurement Units of Length
Despite the convenience of ancient units, their varying nature and lack of uniformity posed challenges. When an object was measured using a cubit or hand span, its length fluctuated from person to person due to individual differences in body proportions. Consequently, this system of measurement became inconvenient and inaccurate. So, to maintain uniformity in measurement, scientists around the world accepted some of the units as standard units. This set of units is generally referred to as the Standard International or SI system of units. This standardized set of units established uniformity in measurement, laying the groundwork for more precise and universally accepted measurement systems.
Definition of Standard International or SI Unit –
Standard International or SI unit is the unit which is acceptable to majority of the people as a basic unit of measurment.
Standard International or SI units for measurement of length, mass, time, and temperature are given below:
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol |
| Length | Meter | m |
| Mass | Kilogram | Kg |
| Time | Second | s |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
D. MULTIPLE AND SUB-MULTIPLE UNITS
Sometimes, standard units or SI Units are not convenient for expressing the measurement of very large or very small quantities. In such cases, we use multiples or sub-multiples of these standard units.
Let us understand by an example,
To measure the distance between two far-off cities, say Chicago and New York, measuring in meters is not only difficult but also very inconvenient. Hence, we use a bigger unit, say, a kilometer, which is a multiple of a meter.
1 kilometer = 1000 meters
In short, 1 km = 1000 m
Now, instead of saying the distance between Chicago and New York is 1,250,000 m, we say it is 1250 km, which is far more convenient.
Similarly, if we are measuring the length of an eraser or a pen, or say, our nails, we again cannot depend on the unit meter, but we need some smaller or sub-multiple units like centimeter (cm) or millimeter (mm).
1 meter = 100 centimeters or 1000 millimeters
In short, 1 m = 100 cm or 1000 mm
1 cm = 10 mm
So, it is convenient to express the diameter of a coin as 2 cm instead of 0.02 m or the size of the tip of a pen as 1 mm instead of 0.001 m.
Now, kids, as you have learned the basics of measurement, you can proceed to an advanced level by going through my specific posts related to the measurement of length, mass, time, and temperature.