Difference Between Mass And Weight | Kg vs Kgf
Welcome to Selftution.com – the best educational website dedicated to making learning clear and simple. In this lesson, we’ll clarify the common misconceptions about the difference between mass and weight, including Kg versus Kgf.
Mass and weight are two common science terms that people often mix up. Kids especially use them interchangeably without understanding that there is a difference between mass and weight. Yes, it’s true—mass and weight are different.
Definition of Mass and Weight:
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, whereas weight is a force exerted by an object of fixed mass due to gravity.
Before discussing the differences between mass and weight, let’s learn more about each one.
Skip to >> The difference between mass and weight.
Topics covered:
- Mass
- Weight and its SI unit
- Difference between mass and weight
MASS
Mass is the measure of the total amount of matter in an object. Everything around us is made up of tiny particles called atoms or molecules. In some substances, these particles are packed more tightly than in others. The more atoms or molecules an object has, the greater its mass. For example, a heavy rock has more mass than a small pebble because it has more atoms or molecules packed into it. Thus, mass depends on how much matter or how many atoms and molecules an object contains.
A definition of mass for kids:
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter present in an object.
Let us understand it with this simple exercise –
Exercise
Take two empty glasses of the same size. Fill one glass to the top with sand and the other with water. Now lift each glass one by one. Which one feels heavier? You will notice that the glass with sand is heavier than the glass with water.
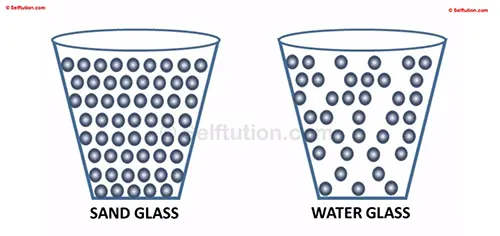
Number of Atoms in Sand and Water
This is because sand, being a solid, contains more atoms packed closely together when compared to liquid water. So, even though both glasses are the same size, the glass filled with sand has more atoms and therefore more mass than the glass filled with water. In other words, the glass with sand has a greater mass than the glass with water.
So, mass measures the amount of matter in an object. If we compare two objects of the same volume, the one with more atoms or molecules will have more mass.
STANDARD UNIT (SI) FOR MEASUREMENT OF MASS
We measure mass in kilograms. The kilogram is the Standard International System (SI) unit of mass. In short form, we write it as (kg).
When you visit a shopkeeper and ask for 1 kilogram of sugar, you specify the amount you need by its mass—1 kilogram. The shopkeeper uses a balance scale to measure exactly 1 kilogram of sugar before giving it to you. In this case, mass is the basic measurement of quantity, the balance scale is the tool used to measure it, and the kilogram (kg) is the unit of measurement.
To know how big 1 kilogram or 1 kg is, visit the shop of the nearest grocer and request him to show you a 1-kilogram mass. Kindly note this mass is commonly mistaken for weight.
MULTIPLES AND SUB-MULTIPLES OF KILOGRAM (kg)
The unit kilogram (kg) is too small for measuring some masses and too large for others. So, we increase it in multiples of 10 for large measures and decrease it by sub-multiples of 10 for small measures. These multiples and sub-multiples of the kilogram are:
Multiples of kilogram
Quintal, 1 quintal = 100 kilograms = 100 kg
Metric Tonne, 1 metric Tonne = 1000 kilograms = 1000 kg
To measure the mass of massive objects like stars and galaxies, we use the solar mass as the unit. The solar mass is defined as the mass of the Sun.
Sub-multiples of kilogram
Gram (g), 1 g = 0.001 kilograms = 1.0 x 10-3 g or 1 kg = 1000 g
Milligram (mg), 1 mg = 0.000001 kilograms = 1.0 x 10-6 g or 1 kg = 1000,000 mg
To measure the mass of microscopic objects like atoms or molecules, we use the atomic mass unit (amu or u) as the unit. The atomic mass unit (u) is 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom, approximately 1.66×10−27 kg.
WEIGHT
Force exerted by an object of fixed mass under the influence of gravity is called weight.
WEIGHT = MASS X GRAVITY
The weight as a force is measured in the SI unit called “Newton (N)”. On Earth, the gravitational pull exerts a force of approximately 10 N on a mass of 1 kilogram. This means a body of mass 1 kg will weigh 10 N on the Earth due to gravity. However, it’s common for people to mistakenly use kilograms (kg) as the unit for weight. This confusion stems from another unit of weight known as “kilogram-force (kgf)”, where 1 kgf is nearly equal to 10 N. So, a body with a mass of 1 kg will weigh nearly 1 kgf or 10 N on Earth.
A definition of weight for kids:
Weight is a force exerted by object of fixed mass under influence of gravity.
The weight of an object changes in different locations around the Earth due to variations in gravity, while its mass remains constant. Although the difference in gravity across Earth’s surface is typically minimal, resulting in unnoticed changes in an object’s weight, this becomes more evident when we venture outside Earth, such as on the moon.
Difference between the Mass and Weight of the Moon and the Earth’s Surface
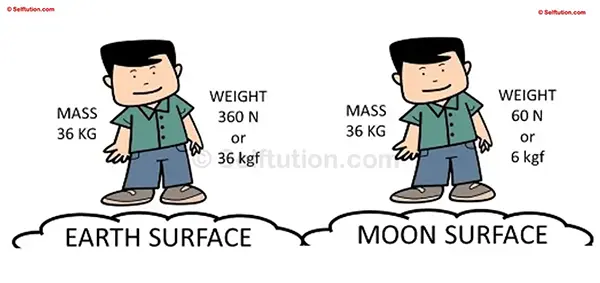
Difference between Mass and Weight on the Moon and the Earth’s Surface.
The gravitational force of Earth exerts approximately 10 Newtons or 1 kilogram-force (kgf) on a mass of 1 kilogram. So, if your mass is 36 kilograms, your weight on Earth would be 360 Newtons or 36 kgf. However, on the moon, gravity is about 1/6th that of Earth’s. Thus, your weight on the moon would be only 60 Newtons or 6 kgf, calculated as 360 multiplied by 1/6. Despite the weight change, your mass remains constant at both places, as your body contains the same number of atoms on the moon as it does on Earth.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MASS AND WEIGHT
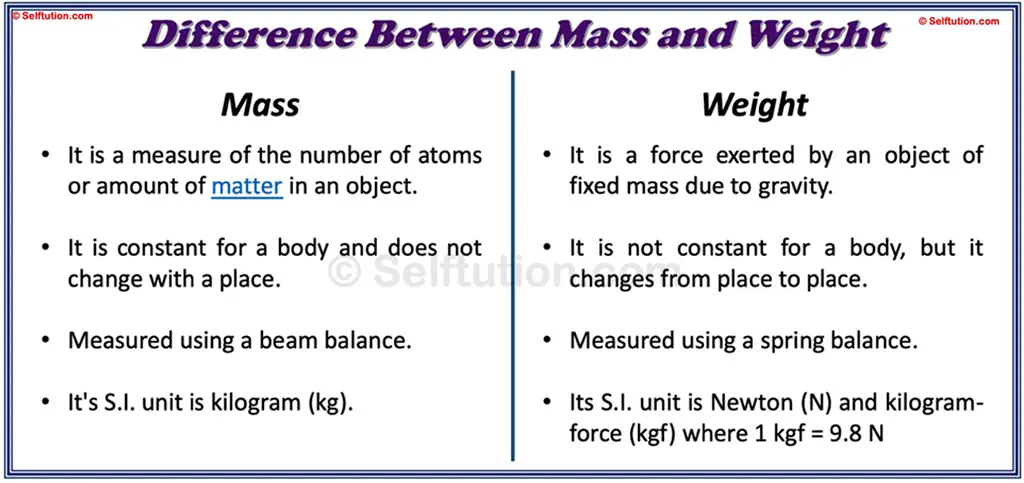
- Mass is a measure of the number of atoms or amount of matter in an object, whereas weight is a force exerted by an object of fixed mass due to gravity.
- Mass remains constant for a body and does not change with place, whereas weight changes from place to place.
- To measure mass, we use a beam balance, whereas for weight, we use a spring balance.
- Mass is a scalar quantity, whereas weight is a vector quantity.
- S.I. unit of mass is the kilogram (kg), and that of weight is Newton (N). Another unit of weight is kilogram-force (kgf), where 1 kgf = 10 N (nearly)
Difference between mass and weight in the tabular form:
Difference between Mass and Weight