Latitude horizontal or vertical? Definition & Important Latitudes
Latitude: Horizontal or Vertical? Clear Definition, Key Lines (Equator, Tropics, Poles), and Why It Matters | Selftution.com
Trusted by students worldwide, Selftution.com is the best educational website for breaking down complex geography topics into simple, visual lessons. Welcome to your ultimate learning hub!
So, let’s begin.
Latitude and longitude are imaginary lines drawn on a globe to help us pinpoint the exact location of any place on Earth. A common question that kids often ask is, “Is latitude horizontal or vertical?”
This post will clarify this confusion and explore the key differences between latitude and longitude.
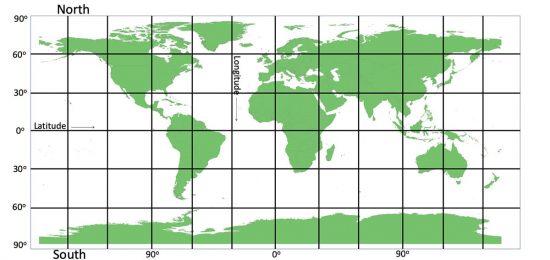
To start, latitudes are horizontal lines, while longitudes are vertical lines. These imaginary lines work together to create a grid system that allows us to locate places on the Earth’s surface.
A globe, which represents the Earth, rotates on its axis, tilted at 23.5 degrees. This axis has two endpoints: the North Pole at the top and the South Pole at the bottom.
By using these horizontal and vertical lines on a globe, we can accurately determine the position of any location in the world.
These lines are imaginary. The horizontal line is Latitude, and the vertical line is Longitude.
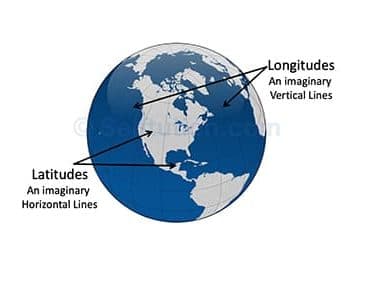
Imaginary horizontal and vertical lines marked on a globe are called latitude and longitude
Topics Covered:
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Units of Latitude and Longitude
- Difference between Latitude and Longitude
- How to locate a place using Latitude and Longitude
LATITUDE
Definition of Latitude
Latitude is an imaginary circles running horizontally from east to west on a globe.
These imaginary circles are parallel to each other, so they are also called Parallels of Latitude. We measure latitudes in the unit degrees (o).
Equator
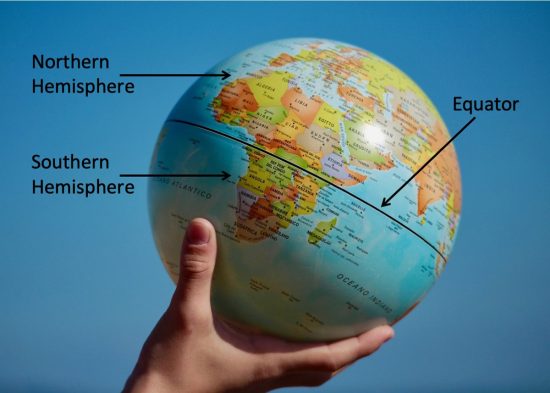
Equator is an imaginary line which is midway between the North Pole and the South Pole, running from east to west.
The equator is the longest latitude. It divides the Earth into two halves called the Hemispheres. The part of the Earth from the equator to the North Pole is called the Northern Hemisphere, and the other part, from the equator to the South Pole, is called the Southern Hemisphere.
Numbering Latitude
We measure latitude units of degrees (o) from the equator to the poles. The Equator is the 0o latitude. We draw other parallels of latitudes at an interval of 1o. The north pole is 90oN and the south pole is 90oS. We mark latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere as 5oN, 10oN, 25oN, 60oN, and so on. In the Southern Hemisphere, we mark them as 5oS, 10oS, 25oS, 60oS, and so on.
There are 181 latitudes in total – 90 latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, 90 latitudes in the Southern Hemisphere, and the Equator is the 0o latitude.
Important Latitudes
The most important latitude is the equator, marked at 0o. There are six other important latitudes, which are as follows:
- The North Pole is marked at 90 ° N
- The South Pole is marked at 90 °S
- Tropic of Cancer at 23.5 °N
- Tropic of Capricorn at 23.5o S
- Arctic Circle at 66.5 °N
- Antarctic Circle at 66.5 oS
For the exact measurement of important latitudes, click here.
Important Facts about Latitudes
- Latitude runs from east to west at an equal distance from each other.
- As we move from the equator to the poles, the length of latitudes decreases.
- All the latitudes are complete circles, except the North Pole and the South Pole. They are just two points.
LONGITUDE
Definition of Longitude
Longitude is an imaginary circle running vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole.
They specify the east-west position of a point on the Earth’s surface. Longitude is also called the Meridian. It is from this word ‘meridian’ that we use the words anti-meridian (a.m.), which means ‘before noon‘, and post meridian (p.m.), which means ‘afternoon‘.
We measure longitude in units of degrees (o).
Prime Meridian / Greenwich Meridian
Prime Meridian or Greenwich Meridian is the 0o longitude which passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, near London.
Numbering Longitude
There are 360 meridians or degrees of longitude. Prime Meridian or Greenwich Meridian is the 0o longitude. We draw other meridians or longitudes at an interval of 1o. There are 180 degrees of longitude to the east of the Prime Meridian (marked as 1oE to 179oE). Similarly, there are 180 degrees of longitude to the west of the Prime Meridian (marked as 1oW to 179oW). The 180 °E and 180 °W longitudes meet and form a single line called the International Date Line. It passes through the islands of the Pacific Ocean. When we cross the international dateline, a new date begins.
Important Facts about Longitudes
- Longitudes are of the same length, meeting at the poles.
- They cut latitude at right angles (90o).
- They are the farthest from each other at the equator and come closer as we move away from the equator and go towards the poles. Finally, they meet at the North and South Poles.
UNITS OF LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE
The primary unit in which we measure longitude and latitude is degrees (°). There are 360 longitudes (180° E to 180° W) and 180 latitudes (90° N to 90° S). Thus, for measuring a more precise location, we divide each degree into 60 minutes (’) and, in turn, each minute into 60 seconds (”). For finer accuracy, fractions of seconds given by a decimal point are used.
1° = 60’ = 3600”
Thus, the exact measurement of important latitudes comes out to be:
- Tropic of Cancer at 23° 26′ 12.1″ N
- Tropic of Capricorn at 23° 26′ 12.1″ S
- Arctic Circle at 66° 33′ 47.9″ N
- Antarctic Circle at 66° 33′ 47.9″ S
Here, it is important to understand that due to the oblate shape of the Earth, distance varies among latitudes and longitudes.
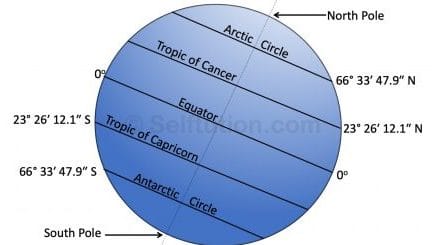
Important Latitudes with Exact Measurement in degrees, minutes, and seconds
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE
- Latitude is horizontal, whereas longitude is a vertical line.
- Latitude runs from east to west, whereas longitude runs from the North to the South Pole.
- The length of a latitude varies with its distance from the equator, whereas it remains the same for longitude. At the North Pole and the South Pole length of the latitudes becomes zero.
- Latitudes are parallel to each other, whereas the distance among longitudes varies. Longitudes are the farthest from each other at the equator and come closer as we move away from the equator.
HOW TO LOCATE A PLACE USING LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE
To locate a place using latitude and longitude, we require a grid.
A Grid is a network of lines, which forms when latitudes and longitudes cross each other.
This grid helps us to locate a place. For example, if we know the latitude and longitude of a place, the point at which they intersect is the location of that place.