Universe for Kids: Introduction to Cosmos
Introduction to the Universe or the Cosmos for Kids
Welcome to Selftution.com – the best educational website for students and learners seeking clear, simple explanations of science, math, and other school subjects.
So, let’s begin.
In this post, we’ll introduce young minds to the wonders of the cosmos and help them explore the basics of our amazing universe.
Definition/meaning of the Universe for kids-
The universe is a wide-open space that holds everything we see in the sky, including our home, the Earth.
INTRODUCTION TO THE UNIVERSE OR THE COSMOS FOR KIDS
At least once in our lives as kids, every one of us has looked into the night sky and wondered what it might hold. Is it just the Moon and twinkling stars or something more bizarre than our expectations?
Away from our daily life here on Earth, the Universe is a weird and truly wonderful place. Here, stars take birth and explode. Star clusters, called galaxies, fly away from each other. The straight path of light is bent, and time goes faster or slower. Modern science explains some of these mind-boggling events – but not all. The more we learn about the universe, the stranger it gets.

The Milky Way is our home. Image Courtesy www.pixabay.com
TOPICS COVERED:
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE UNIVERSE AND THE COSMOS
The meaning of the Cosmos and the Universe is somewhat similar to each other, with minor differences between the two. We derive the word cosmos from the Greek language, where it has two meanings: “order” and “world“. Thus, cosmos means “the world in order“. It considers everything we see or observe in the sky or on the earth as part of an orderly system and follows certain rules harmoniously. Whereas the meaning of the Universe is much simpler when compared to that of the Cosmos. It states that everything around us, including the Earth, is part of the Universe.
Nowadays, the meaning of Cosmos doesn’t include the idea of the world in order. Thus, the word “Cosmos” is synonymous with “Universe”.
Cosmology is the study of the origin and development of the Universe. We derive the word cosmology from two Greek words: “cosmos” meaning “world” and “logy” meaning “study”.
EXPLORATION OF THE UNIVERSE AND THE COSMOS

Flat Earth Vs Round Earth
In ancient times, people believed that the Earth was flat and the center of everything. Gradually, they learned that it was not flat, but ball-shaped, and is just one of the eight planets that travel around our star, the Sun. And the Sun is just an ordinary star, like many millions of others in the Universe. Early astronomers simply used their naked eyes to explore the night sky and study the Universe. However, modern astronomers looked through big, powerful telescopes and found other bizarre celestial objects in the Cosmos, like meteors, asteroids, comets, galaxies, nebulae, supernovae, black holes, magnetars, neutron stars, etc. All the objects that we see in the sky are called celestial objects.
Back to >>the Introduction to the Universe for kids
WHAT IS THE SIZE OF THE UNIVERSE?
No one knows what is the size of the Universe and how big it is. It may have an end, which is too far away to detect, or it may have no end at all. It may even curve around on itself, so it is endless like a circle. But we do know that it is the biggest thing we know and includes all the empty parts of space between the stars. Most scientists think that the Universe or the Cosmos began with a gigantic explosion – the Big Bang, which happened billions of years ago. Since then, it has been growing in size, bigger and bigger in all directions, creating more and more space.

Representation of the Big Bang
STARS
There are countless billions of stars in the Universe. Each star is a huge, fiery ball of gas, mostly hydrogen, like our Sun. Yes, our Sun is also a star, and it is 109 times bigger than the Earth. Stars other than the Sun appear as tiny dots in the sky because they are very far away from us. To know more about stars, click here
THE SUN
The Sun is a star. It is located at the center of our solar system. It is about 150 million kilometers away from Earth. Being nearer to the Earth than any other star, it looks big and bright, like a ball of fire. It is the largest and the heaviest member of the solar system. It is about 109 times bigger than the Earth, with a diameter of about 13,92,000 kilometers. Its mass is about 3,33,000 times that of the Earth. The temperature of the outer surface of the Sun is nearly 6000 °C, which is enough to melt almost any substance. To learn more about the Sun, click here
Back to >>the Introduction to the Universe for kids
PLANETS
The word ‘planet‘ is derived from the Greek word ‘wanderer‘ as they revolve around the Sun. There are eight planets in our solar system. They move around the Sun in elliptical orbits. In order of their distance from the Sun, they are – Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. As planets comprise solid material and gases, they do not have their own heat and light. They shine with the light reflected from the Sun.
Kids often ask – What is our Solar System called? The reason behind this particular question is that our Solar System is not unique in the Universe. Other stars also have a somewhat similar planetary system around them. We call them stellar systems. The word ‘stellar’ means ‘relating to a star or stars”. However, as we derive the name of our star from the Latin word ‘Sol’, we call our stellar system the Solar System. For quick facts about the planets, click here.
SATELLITES

Artificial Satellite
Satellites are small bodies that revolve around the planets. They are of two types: natural and artificial. The moon is a satellite of the Earth, and it is a natural satellite. An artificial satellite is a man-made object that orbits the Earth or other planets. Like planets, satellites also do not have any heat or light of their own. They shine by reflecting the light from the Sun. The Earth is not the only planet that has a natural satellite or the Moon. Mars has two, Jupiter has 63, Saturn has 34, Uranus has 27, and Neptune has 13 natural satellites. Ganymede is the largest natural satellite of Jupiter, while Titan is the largest satellite of Saturn. To learn more about satellites, click here.
Back to >>the definition/meaning of the Universe/cosmos for kids
GALAXIES

Location of the Solar System in the Milky Way Galaxy
Billions of stars together make a galaxy. As our Sun is a star, it is also a part of a galaxy. We call it the Milky Way. Our Galaxy is not the only one in the Universe or the Cosmos. It is just one of the countless millions of galaxies out there. Galaxies are not spread evenly through the Universe. They are clumped together in clusters of anything from half a dozen to several thousand. Our Galaxy is part of a neighborhood cluster of 3,000 galaxies, the local group.
There are several different shapes of galaxies – spiral, elliptical, barred spiral, irregular, etc. Our galaxy is a spiral. It is a vast collection of 100 billion stars, about 1,06,000 light-years across. From the Earth, it appears as a pale streak of light stretching across the night sky. It almost seems like someone has spilled milk across the sky, which is why it is called the Milky Way. To know more about galaxies, click here.
NEBULAS

Carina Nebula
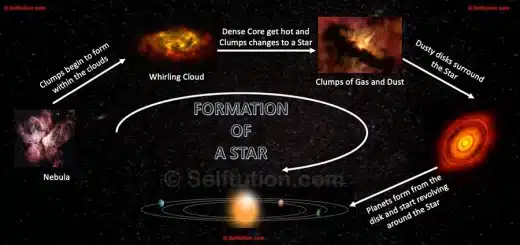
A nebula or nebulae, named from the Greek word ‘cloud‘, is a vast interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, and other gases spread across the universe. Like clouds in the sky, nebulas come in interesting shapes like flowers, fingers, etc. The nebula is a region where stars are born. In this huge area of hydrogen gas, gravity pulls gas and dust together to form clumps. As each clump pulls itself tighter, it begins to get hot. If the clump reaches a temperature of 10 million oC, nuclear fusion begins, and the clumps change to glowing stars. Whatever is left forms planets that revolve around the Star. The most famous nebula in space is the Orion Nebula. The Orion nebula is the most active area of star formation in our galaxy. To know more about nebula, click here.
Back to >>the definition/meaning of the cosmos for kids
SUPERNOVAS
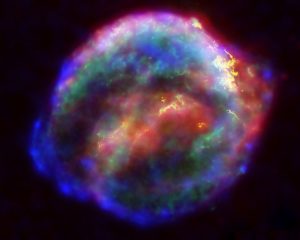
Kepler’s supernova
A supernova is a giant explosion generated by a dying star. For a few weeks, it shines with the brightness of millions of Suns. In a medium-sized star, the heat tries to make the star bigger, but gravity balances this expansion and tries to shrink it. So the star stays the same size and glows steadily. At the core of the star, hydrogen fuses to form helium. When hydrogen exhausts, the core shrinks and begins fusing helium to form other heavy elements. The outer layer of gas cools and swells, and it becomes a red giant. In the biggest stars, more changes take place in the core, and the star suddenly takes in energy instead of giving it out. It collapses in seconds. The collapse of a huge star is like a giant nuclear explosion called a supernova. To know more about supernovas, click here.
WHITE DWARFS
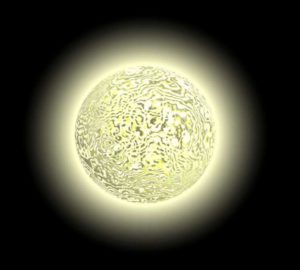
White Dwarf
All stars in the Cosmos do not die in a magnificent explosion, a supernova. A small star, when it runs out of hydrogen, gradually cools and shrinks into a white dwarf and dies somewhat silently. As a rule of thumb, stars with a mass less than 8 times our Sun will form white dwarfs. When stars get old, hydrogen in their core is exhausted, and the star begins to fuse helium to form heavier elements. While doing so, it starts shedding its outer layer. When this process is over, what remains is its core, and a white dwarf is born. The mass of the white dwarf is around 1.45 times that of the former star. To know more about white dwarfs, click here.
Back to >>the definition/meaning of the Universe for kids
NEUTRON STARS

Neutron Star
When a star dies in a supernova, it forms a neutron star. As a rule of thumb, after a supernova, a star with a mass between 8 to 20 times that of our Sun will end up as a neutron star. The supernova blows off all the star’s layers, except the iron core. The gravity of the iron core shrinks it further to such an extent that protons and electrons fuse, and we are left with only neutrons. At this time, the core of the star is about 20 kilometers wide, and we call it a neutron star. Even with this size, the neutron star has a mass of 1.5 to 5 times the mass of our Sun. To know more about neutron stars, click here.
PULSARS
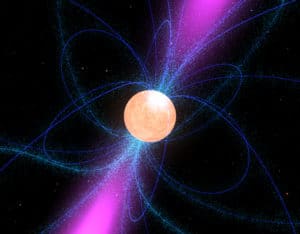
Pulsar Star
A pulsar is a highly magnetized, rotating neutron star. It sends out powerful electromagnetic and radio signals as regular pulses, like a flashing beacon across the Universe. Pulsars in the Universe can be more easily correlated with a lighthouse on Earth. They are a few kilometers across and spin insanely fast. The fastest known pulsar is rotating with a record speed of 1100 rotations per second. To know more about pulsars, click here.
Back to >>the definition/meaning of the Universe for kids
MAGNETARS

Magnetar Star
Magnetars are a type of neutron star, like pulsars, but with an extremely powerful magnetic field. They are one of the densest objects in the Cosmos. They convert heat and rotational energy into a very strong magnetic field. The magnetic field made by a magnetar is a quadrillion times stronger than that of the Earth. During a supernova, the spin, temperature, and magnetic field of the neutron star determine whether it will be a pulsar or magnetar. As per estimate, about one in ten supernova explosions results in a monetary rather than a more standard neutron star or pulsar. To know more about magnetars, click here.
BLACK HOLES

A Blackhole emitting radiation
Black holes are the weirdest objects in the Universe or the Cosmos. Until now, a black hole is just a theory, and we hardly know anything about it. But whatever we know makes it more and more strange.
Black holes are objects in the Universe where the gravity is so strong that it sucks in everything, including light. As even light could not escape a black hole, that’s why they appear black. So, how do we know black holes exist? We can identify a black hole by observing the light and the objects around it. Black holes are formed when a star of mass more than 20 times that of our sun dies in a supernova. They are the heaviest objects in the Universe. To understand the density of a black hole, imagine a grain of rice with the mass of the Earth. To know more about black holes, click here.
Back to >>the definition/meaning of the Universe for kids