Different Forms of Energy in Physics and Examples
Explore the Different Forms of Energy in Physics – Mechanical, Thermal, Chemical & More with Real-World Examples
Selftution.com – The #1 Free Educational Platform for Clear, Simplified Learning. Master physics concepts effortlessly with detailed explanations, interactive diagrams, and practical examples. Welcome to the best way to learn!
In this post, we will learn about the different forms or types of energy studied in physics with examples.
In Physics, we define energy as the ability or capacity to do work. As per the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor destroyed; however, it can be changed from one form to another.
Different Forms of Energy
- Mechanical energy,
- Heat or Thermal energy,
- Light energy,
- Chemical energy,
- Sound energy,
- Magnetic energy,
- Electrical energy, and
- Atomic or Nuclear energy
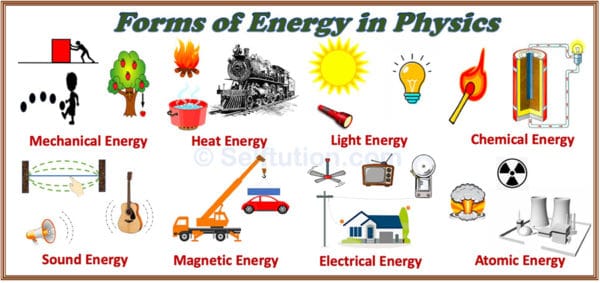
Different Forms or Types of Energy in Physics with Examples
Forms of Energy in Physics
Different forms of energy in physics are listed below:
1. MECHANICAL ENERGY
Mechanical energy is the energy possessed by a body due to its state of rest or state of motion. Mechanical energy is of two forms – potential and kinetic. The total mechanical energy of a body is the sum of the potential and kinetic energies.
The form of energy possessed by a body due to the virtue of its state of motion is called kinetic energy. Whereas, potential energy is the stored-up energy of a body due to the virtue of its state of rest or the position that can do the work. Some examples of these two forms of energy are as follows:
- A fast-moving stone thrown toward a glass window can break a window pane when it strikes the pane. Thus, the stone in motion has kinetic energy. Some more examples of kinetic energy are – a bullet fired from a gun, a rolling ball, an orange falling from a tree, flowing water, a boy playing football, a swinging pendulum, a wind blowing, a flying bird, etc.
- Water stored in a dam has potential energy stored in it. The water has energy due to its position at a height. When we open the gates of the dam, the water flows through the turbine and produces electrical energy.
- A wound-up watch spring has potential energy because of the wound-up state of its coil. As the spring unwinds, it does work to move the arms of the watch.
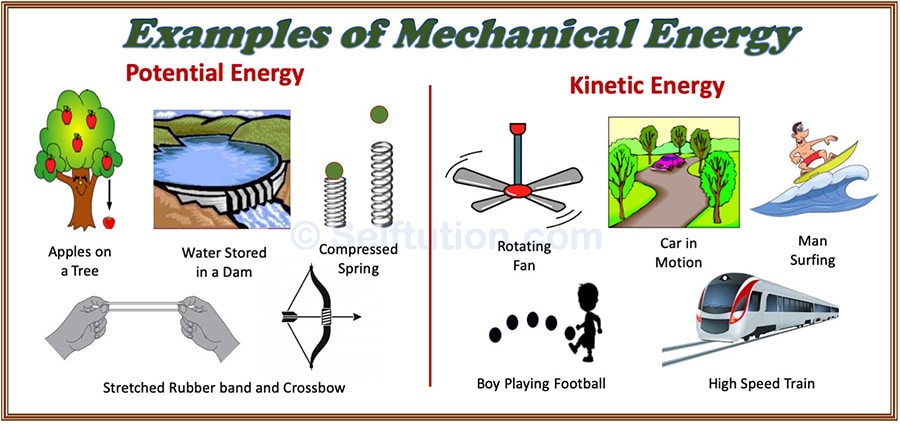
Examples of Mechanical energy – Potential and Kinetic energy
2. HEAT OR THERMAL ENERGY
Most forms of energy get converted into heat energy before they are used. So, it is one of the most important forms of energy. The energy released when we burn coal, oil, wood, or gas is called heat or thermal energy. Like other forms of energy, we can use heat energy to carry out the work. Let’s understand the same with an example:
Steam possesses heat energy; thus, it is capable of doing the work. It is our common experience that if we heat some water in a kettle with a lid on it, we notice that as the water begins to boil, the steam makes the lid lift. This is actually due to the heat energy stored in the steam. Based on this, James Watt in the year 1765 invented the steam engine. In the steam engine, James Watt used heat energy to drive the train.
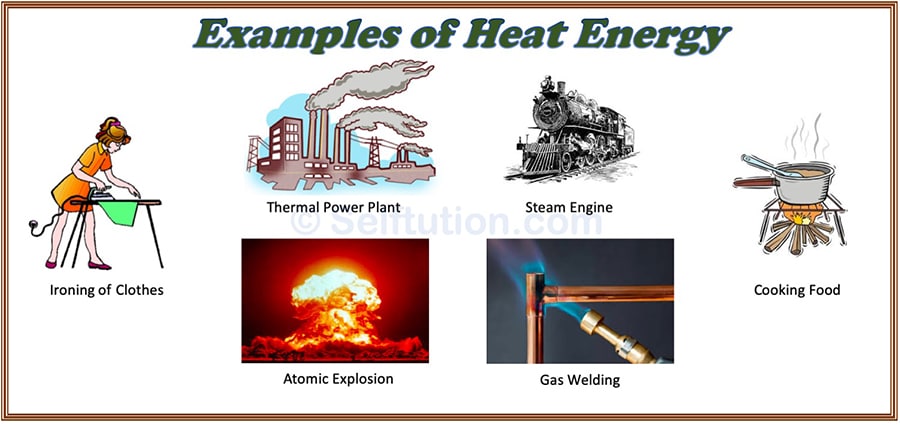
All forms of energy are mostly converted to heat or thermal energy before they are put to use.
3. LIGHT ENERGY
Light is a form of energy in the presence of which we can see objects. Under normal circumstances, light always travels in a straight line, i.e., it has a rectilinear propagation, which also leads to the formation of the shadow of opaque objects. Most importantly, light is also a very good source for starting chemical reactions. Some examples of the usage of light as energy are:
- In the process of photosynthesis, plants produce food (glucose) from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight.
- Light consists of very small packets of energy called photons. These photons travel at very high speed – in fact, nothing in the universe travels faster than photons. These photons can move small particles. However, we do not feel the light energy because ordinary light does not move the objects around us. But a strong beam of light can move small particles like electrons.
- When light travels from an object to our eyes, we can see the object. It helps us to identify colors.
- By using photovoltaic cells, we can convert light energy from the Sun to electrical energy.

Source and Use of Light Energy
4. CHEMICAL ENERGY
Chemical energy is the energy stored in matter. Matter releases this energy during chemical reactions. For example, fuels like coal, petrol, diesel, and kerosene oil all have chemical energy stored in them. However, they release this chemical energy only during the combustion reaction in the form of heat. The chemical energy released by petrol or diesel helps to run a car or a truck. Some more examples of chemical energy are:
- When we eat food, our body processes the food particles to release chemical energy. This energy helps us to do work and keeps us warm.
- In chemical batteries, we convert chemical energy to electrical energy to perform various kinds of work.
- By combustion of various fuels in the presence of oxygen, we convert chemical energy to produce heat and light energy.
- In a thermal power plant, we convert the chemical energy of coal into electrical energy.

Examples of Chemical Energy
5. SOUND ENERGY
When any object vibrates, it produces sound energy. When sound produced by a vibrating body reaches our eardrum, it makes the drum vibrate, and we hear the sound of the vibrating body. Remember, not all vibrations are audible to human ears. A very high amount of vibrations (more than 20,000 vibrations per second) or very low vibrations (less than 20 vibrations per second) produce such a sound that is inaudible to human beings. However, animals like bats, rats, and moths can hear vibrations of more than 20,000 per second.
Since vibrating or moving bodies have kinetic energy so sound too is a kind of energy. However, unlike other forms of energy, it needs the presence of a medium to propagate. This is the reason why two astronauts fail to hear each other on the moon’s surface due to the absence of any medium. Some examples of sound energy are – an airplane taking off, a buzzing of a bee, a speech by a woman, the ringing of a bell, the popping of a balloon, etc.
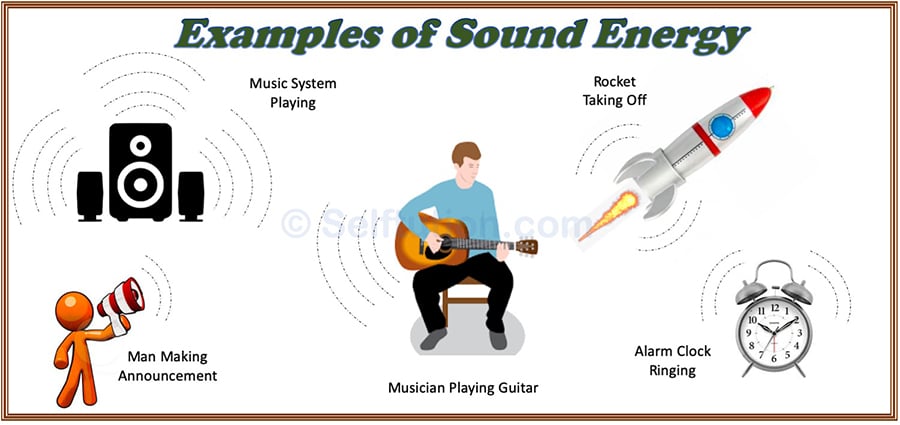
Examples of Sound Energy
6. MAGNETIC ENERGY
Magnetic energy is the energy possessed by a magnet. A magnet can attract iron nails from a distance, and thus, the force exerted by the magnet makes the nail move toward the magnet. Therefore, magnetic energy can work from a distance. Since a magnet can move particles, it possesses one of the forms of energy. Some examples of magnetic energy in daily life are:
- In factories, to separate iron scrap from the heap of waste material, we use the big electromagnets fixed in the cranes.
- An electric motor used in a fan or other machines has magnets in it; thus, it utilizes magnetic energy.
- We can produce electrical energy by rotating a coil made of copper or any other conductor in a magnetic field. This is the principle behind the working of generators.
7. ELECTRICAL ENERGY
When we rub two bodies together, they produce opposite charges (positive and negative), carrying electrical energy. This is static electrical energy. However, if we connect these two bodies with opposite charges via a conductor, an electric current flows through the conductor. We call this electricity.
Out of all the other forms of energy we study in physics, electrical energy is of tremendous use in our daily lives. We use electricity at home to run our domestic appliances, at offices, in factories, for transportation, etc. Today, electricity is a basic necessity of life. Life will come to a standstill if electricity fails to exist for quite some time. Examples of appliances in which we use electrical energy are – lightning, fans, televisions, computers, air conditioners, doorbells, geysers, microwave ovens, etc.
8. ATOMIC OR NUCLEAR ENERGY
Energy stored in the nucleus of atoms is nuclear or atomic energy. A large amount of energy is produced when the nucleus of an atom splits (nuclear fission) or two nuclei of different atoms combine (nuclear fusion). During nuclear fission, atoms or nuclei of some of the heavy elements like uranium, thorium, or polonium split to form other stable elements. Whereas in nuclear fission, atoms or nuclei of small atoms like hydrogen and helium combine to form bigger atoms. During these processes, elements change into other elements by releasing a large amount of energy in the form of heat along with radiation. We can use atomic energy for peaceful as well as destructive purposes. Some of the examples of usage of atomic or nuclear energy are:
- During nuclear fission or nuclear fusion, a large amount of energy is released in the form of heat. We can use this energy to generate electricity in nuclear reactors.
- The radiation emitted in the form of nuclear energy helps in the medical treatment of diseases such as cancer.
- For destructive purposes, we use atomic bombs to destroy the enemy in the war.
Out of all the other forms of energy we study in physics, nuclear energy is the most destructive one, if not put to use correctly.
You may also like…... Types of Chemical Reactions in Chemistry