Difference Between Speed And Velocity With Examples
For a body in motion, both speed and velocity are measures that help us understand how fast it is moving. While they may seem similar at first glance, there are key differences between the two.
This post will delve into the concepts of speed and velocity and highlight the differences between them.
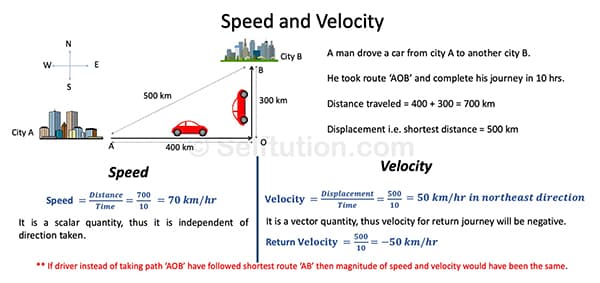
Speed is a physical quantity that indicates how fast an object is moving, regardless of the direction. It represents the rate of motion but does not provide any information about the direction in which the object is traveling.
Velocity, on the other hand, not only measures how fast the object is moving but also specifies the direction of motion.
The fundamental difference lies in the presence of direction. Speed is a scalar quantity, as it has only magnitude, while velocity is a vector quantity, as it includes both magnitude and direction.
In simpler terms, speed tells us “how fast,” while velocity tells us “how fast and in which direction.“
Skip to the difference between speed and velocity
SPEED
Definition of Speed –
The speed of a body is the rate of change of distance or the distance traveled by the body in unit time.
It is a scalar quantity. We represent it by the small letter ‘u’ or ‘v’ in italics as ‘u’ or ‘v’. If a body travels a distance ‘S’ in time ‘t’ then the formula for speed ‘v’ is
Speed = Distance / Time
or
v = S / t
S.I. Unit of Speed –
Since the S.I. unit of distance is the meter (m) and time is second (s), thus, the S.I. unit of speed is the meter per second or m/s (ms-1).
VELOCITY
Definition of Velocity –
The velocity of a body is the displacement of the body in unit time or the distance traveled by it in a unit time in a particular direction or the rate of change of displacement of a body.
It is a vector quantity. We represent it by the small letter ‘u’ or ‘v’ in bold as ‘u’ or ‘v’. If the displacement of a body is ‘S’ in time ‘t’ then the formula for velocity ‘v’ is
Velocity = Displacement / Time
or
v = S / t
Note: For velocity, both magnitude and direction need to be specified. The two bodies move with the same velocities when they move at the same speed and in the same direction. However, velocities are different if both are moving at the same speed in an opposite or any other direction.
S.I. Unit of Velocity –
As the S.I. unit of both distance and displacement is the same i.e. meter (m). Therefore, the S.I. unit of both velocity and speed is a meter per second or m/s (ms-1).
UNIFORM SPEED AND VELOCITY
Uniform Speed
A body is said to be moving with a uniform speed when there is no change in speed with time.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a uniform speed when the rate of change of distance is the same throughout its motion.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a uniform speed if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
Examples of uniform Speed:
- A car cruising on a highway with its speed locked on,
- A ball rolling on a frictionless horizontal surface, etc.

Uniform Velocity
A body is said to be moving with a uniform velocity when there is no change in velocity with time.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a uniform velocity when the rate of change of displacement is uniform throughout its motion.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a uniform velocity if it travels equal distances in a particular direction, in equal intervals of time.
Examples of uniform velocity:
- A car cruising on the highway towards the north with its speed locked on,
- A ball rolling on a frictionless horizontal surface in any particular direction, etc.
NON-UNIFORM SPEED AND VELOCITY
Non-uniform Speed
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform speed when the speed of the body changes with time.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform speed when the rate of change of distance varies throughout its motion.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform speed if it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
Examples of non-uniform speed:
- A car cruising in a busy market street,
- A ball rolling on a rough surface, etc.
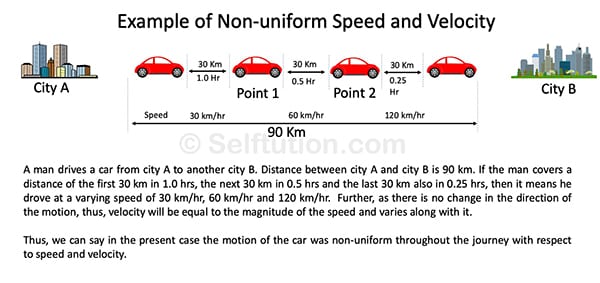
Non-uniform or Variable Velocity
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform velocity when the velocity of the body changes with time.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform velocity when the rate of change of displacement varies throughout its motion.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform velocity if it travels unequal distances in a particular direction, in equal intervals of time.
Or
A body is said to be moving with a non-uniform velocity if it travels equal distances in different directions, in equal intervals of time.
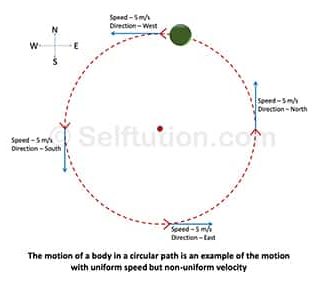 Examples of non-uniform or variable velocity:
Examples of non-uniform or variable velocity:
- The motion of a freely falling body is an example of non-uniform velocity as direction does not change but speed increases continuously.
- Similarly, the motion of a body in a circular path even with uniform speed is an example of non-uniform velocity as the direction of the moving body changes continuously.
When a body moves with non-uniform or variable speed, then we specify the instantaneous speed and the average speed. Likewise, when a body moves with non-uniform or variable velocity, then we specify the instantaneous velocity and the average velocity.
INSTANTANEOUS SPEED AND VELOCITY
Instantaneous Speed
For a body in non-uniform motion, its speed at any instant is called the instantaneous speed. It is the ratio of the distance traveled in a very short interval of time to the time interval. Thus, the formula for instantaneous speed is –
Instantaneous speed = Distance traveled in a short interval of time / Time interval
A speedometer or speed meter is an instrument that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle.
Instantaneous Velocity
For a body moving with variable velocity, the velocity at any instant is called its instantaneous velocity. It is the ratio of displacement of a body in a very short interval of time to the time interval. Thus, the formula for instantaneous velocity is –
Instantaneous velocity = Displacement of a body in a short interval of time / Time interval
To measure instantaneous velocity, the time interval shall be small enough so that the direction of the motion of a body does not change during this interval.
AVERAGE SPEED AND VELOCITY
Average Speed
The ratio of the total distance traveled by a body to the total time taken for the journey is average speed. Thus, the formula for average speed is –
Average speed = Total distance traveled / Total time taken
For a body in uniform motion, the average speed and the instantaneous speed are equal.
Average Velocity
It is the ratio of the displacement of a body to the total time taken for the same. Thus, the average velocity is –
Average velocity = Displacement / Total time taken
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SPEED AND VELOCITY
- The speed is a scalar quantity, while velocity is a vector quantity. The speed and velocity of a body at a given interval of time tell us how fast the body is moving at that time. Velocity provides us with additional information and tells us the direction in which the body is moving.
- For the motion in a straight line magnitude of speed and velocity is the same. However, the speed is always positive, but velocity can be negative or positive depending upon its direction of motion.
- The average velocity of a body can be zero, even when its average speed is not zero.
Difference between speed and velocity in tabular form:
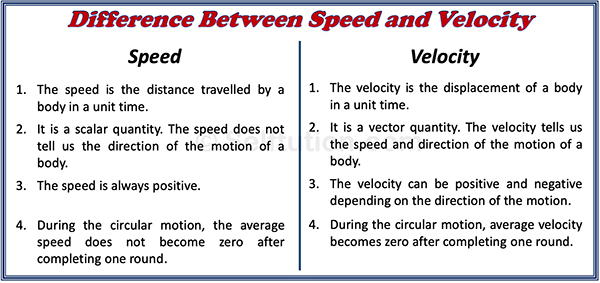
Difference between speed and velocity
For more such information, please visit our YouTube channel SELFTUTION