Cases of Noun: Nominative, Accusative and Possessive
In modern English, there are three cases of nouns; nominative, objective or accusative, and possessive case.
Some people also consider dative and vocative cases of nouns in English grammar, but they are obsolete.
Nominative and Accusative Cases of Noun with Examples
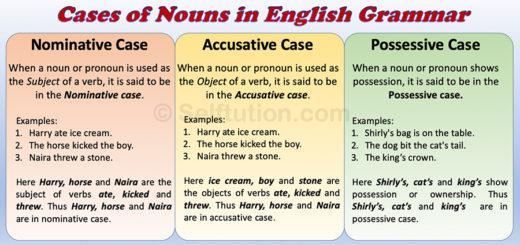
When a noun or pronoun is used as the Subject of a verb, it is said to be in the Nominative case.
When a noun or pronoun is used as the Object of a verb, it is said to be in the Objective or Accusative case.
Let’s understand the nominative and accusative case with these examples: –
- Harry ate ice cream.
- The horse kicked the boy.
In sentence 1,
- The noun Harry is the Subject of the verb ‘ate’. It answers the question, “Who ate ice cream?”
- The group of words ‘ate ice cream’ is the Predicate. The predicate contains the verb ‘ate‘.
- What did Harry eat? – An ice cream. Ice cream is the object that Harry ate. The noun ‘ice cream‘ is therefore called the Object.

Cases of Nouns in English with Examples – Nominative, Objective or Accusative and Possessive Case
So, in sentence 1, Harry is in the nominative case and Ice Cream is in the objective or accusative case.
In sentence 2,
- The noun horse is the Subject of the verb ‘kicked’. It is the answer to the question, “Who kicked the boy?”
- The group of words ‘kicked the boy’ is the Predicate. The predicate contains the verb ‘kicked‘.
- The noun ‘boy‘ is the Object. It is the answer to the question, “Who did the horse kick?”
So, in sentence 2, ‘horse’ is in the nominative case, and ‘boy’ is in the objective or accusative case.
How do you find a Subject or Object in a Sentence?
In my earlier post Subject and Predicate, we learned how to find out the subject of a verb. Here is another tip to help. To find out the subject of a verb, put who or what before it. To find out the object of a verb, add what or whom after it. In both cases, the answers tell you which noun is the subject and object respectively.
Let us understand with examples:-
- Naira threw a stone.
- The question is wrong
- James praised Robert for his honesty.
In sentence 1, who threw a stone? – Naira. So Naira is the subject in the sentence and is in the nominative case. Similarly, Naira threw what? – A stone. So the stone is the object and it is in the objective or accusative case.
In sentence 2, what is wrong? – Question. So the question is the subject in the sentence and is in the nominative case. Similarly, the question is what? – Wrong. So wrong is the object and it is in the objective or accusative case.
In sentence 3, who praised Robert? – James. So James is the subject in the sentence and is in the nominative case. Similarly, James praised whom? – Robert. So Robert is the object and it is in the objective or accusative case.
Possessive Case of Noun with Examples
When a noun or pronoun shows possession, it is said to be in the Possessive case or genitive case.
Let us understand the possessive case with these examples: – The (‘) used to show possession is called an apostrophe.
- Shirly’s bag is on the table.
- The dog bit the cat’s tail.
In sentence 1, Shirly’s bag means the bag possessed by Shirly or the bag belonging to Shirly.
In sentence 2, the cat’s tail means the tail belonging to the cat.
Here, the form of nouns Shirly and cat is changed to Shirly’s and cat’s to show possession or ownership.
Sometimes, the possessive case is used to convey meaning other than possession, like – authorship, origin, kind, etc. Examples of such possessive case are –

Examples of Possessive Case
You may also like…... Types of Chemical Reactions in Chemistry