Movement of the Earth |Effects of Rotation & Revolution
Movement of the Earth: Understanding Rotation & Revolution – Key Effects, Diagrams & Examples
Discover how Earth’s motion shapes our days, seasons, and climate. Selftution.com is the #1 trusted educational website for clear, simplified learning – making science easier than ever!”
Welcome to Selftution.com – Where complex topics become simple!
The movement of the Earth is something we rarely notice while standing on its surface, yet it is constantly in motion. This movement happens in two ways:
- Rotation – The Earth spins on its axis.
- Revolution – The Earth orbits around the Sun.
These simultaneous motions play a crucial role in shaping our environment, influencing everything from the cycle of day and night to the changing seasons.
Effects of Rotation and Revolution
Effects of Rotation:
- Day and night occur due to the Earth’s rotation.
- It causes a change in the direction of wind and ocean currents.
Effect of Revolution:
- It leads to the change in seasons throughout the year.
In this blog, we will explore how these two movements impact life on Earth and contribute to the dynamic nature of our planet. Let’s dive in!
ROTATION
Have you seen a top spinning?
Spinning top – an example of rotation, a movement of the earth
The movement of the earth on its axis is called Rotation. The Earth also spins like a top.
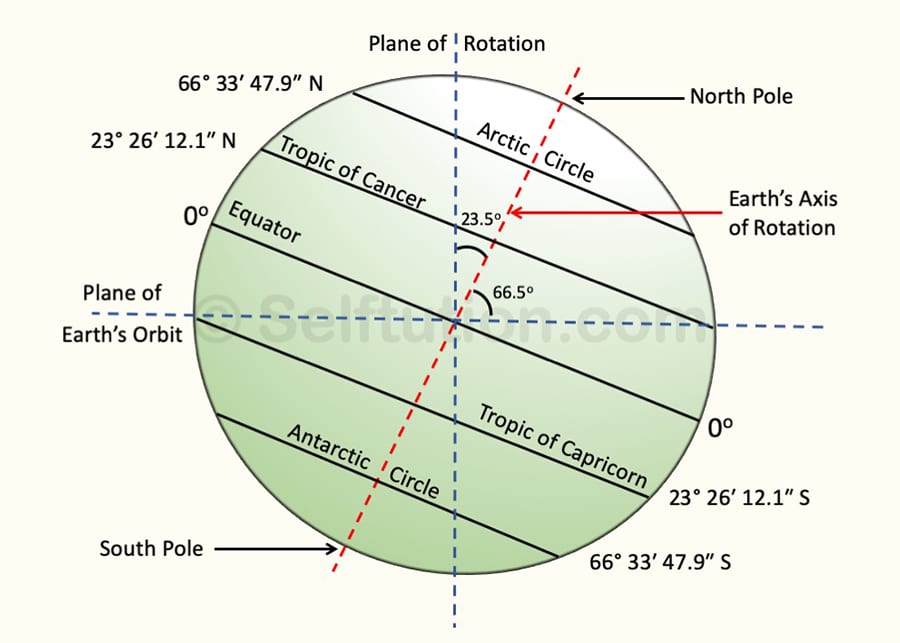
The Earth spins from west to east on an imaginary line or axis passing through its center. This imaginary axis passes through the Geographic North and South Poles and tilts at an angle of 66-1/2° to the plane of the Earth’s orbit.
Effects of the Rotation of the Earth
Some important effects of the rotation of the Earth are:

Position of the Earth during Northern Summer
- The Earth takes 24 hours to complete one rotation around its axis. To be precise, Earth takes 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 40.91 seconds to complete this movement. The rotation of the Earth causes day and night. As the Earth rotates on its axis, the portion of the Earth facing the Sun experiences Day. The other portion, which is away from the Sun, experiences Night. As the Earth continues to rotate, day and night occur alternately.
- The Earth’s rotation affects the direction of the winds.
- It also affects the direction of the flow of water in the oceans.
Japan lies in the extreme east and sees the Sun first. Thus, it is called the land of the Rising Sun. Its time is ahead of places in the West.
REVOLUTION
The movement of the Earth around the Sun in its orbit is called Revolution.While the Earth rotates on its axis, it also moves around the Sun along a fixed elliptical path. This fixed path is called Orbit. Although we might not feel it, the Earth whirls through space at nearly the speed of 30 km/s. The Earth completes this journey around the sun in one solar year, i.e., 365-1/4 days.
The Earth takes 365-1/4 days to complete one revolution around the Sun. To be precise, it is 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, and 45.51 seconds. However, our calendar shows only 365 days in a year. So, what happens to a 1/4 day? So, to correct the same, after every four years, we add this 1/4 day as one extra day to February. This year is known as a leap year with February having 29 days.
Effects of the Revolution of the Earth
One of the most important effects of the revolution of the Earth is that it causes Seasons.
Causes of change in seasons are:
- The revolution of the Earth around the Sun, and
- A fixed inclination (tilt) of the Earth’s axis at an angle of 23-1/2o to its plane of rotation.
As the Earth rotates and revolves around the Sun, one part of the Earth tilts towards the Sun and the other part away from the Sun. The part of the Earth that tilts towards the Sun gets more sunlight and has Summer, whereas the other part away from the Sun receives less sunlight and has Winter. When the North Pole tilts towards the Sun, the Northern Hemisphere experiences the Summer season, and the Southern Hemisphere experiences the Winter season. Similarly, when the South Pole tilts towards the Sun, the Southern Hemisphere experiences the Summer season, and the Northern Hemisphere experiences the Winter season.
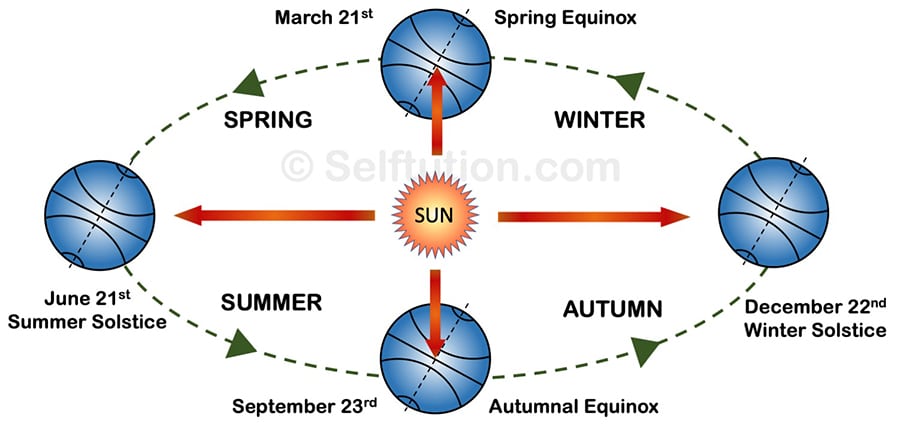
Effects of the rotation and revolution of the Earth – Summer and Winter Solstice, Spring and Autumnal Equinox
The four seasons:
The revolution of the Earth on its tilted axis causes seasons. The Earth experiences 4 seasons in a year: summer, winter, spring, and autumn.
- Spring: On March 21, the Sun is directly overhead the equator. This is the season of spring in the northern temperate zone.
- Summer: On June 21, the Sun is directly overhead the Tropic of Cancer. Thus, during this period, the northern temperate zone experiences summer.
- Autumn: On September 23, the Sun returns to the equator, and the northern temperate zone experiences the season of autumn.
- Winter: On December 22, the Sun is at the Tropic of Capricorn, and the northern temperate zone experiences winter.
In the southern temperate zone, the seasons are the reverse of those mentioned above, at the same time of the year.
Back to…Effects of Rotation of the Earth
OTHER EFFECTS OF ROTATION AND REVOLUTION OF THE EARTH
Equinox and Solstice are the two other effects of the movement of the Earth.
Equinox
‘Equi’ means equal, and ‘nox’ means night, so Equinox means equal day and night. There are two days in a year when the sun shines directly over the equator, and day and night are equal.Equinoxes are those dates when the nights and days are equal. During the movement when both the poles of the Earth are at an equal distance from the Sun, the rays of the Sun fall directly on the equator. Therefore, on this day, the Earth experiences an equinox.
An equinox occurs twice a year, once on March 21 and another on September 23. On March 21, the Earth experiences the Spring or Vernal equinox. On September 23, it is the Autumnal Equinox.
Solstice
‘Sol’ means Sun, and Solstice means the standing still of the Sun. There are two days in a year when the Sun shines brightly on the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.The solstice is the time of the year when the difference between the length of days and the length of nights is the largest. During these days, the sun shines vertically over the tropics. On June 21, the Sun shines directly on the Tropic of Cancer. All the places in the Northern Hemisphere experience their longest day on this date. This is called the Summer Solstice.
When the South Pole tilts towards the Sun, the Southern Hemisphere experiences the summer season, and the Northern Hemisphere experiences the winter season. The Sun shines brightly on the Tropic of Capricorn. On December 22, the Northern Hemisphere experiences the shortest day. This is the Winter Solstice. The reverse is true in the case of the southern region.
Back to…Effects of Rotation of the Earth
Back to…Effects of the Revolution of the Earth
You may also like…... Types of Chemical Reactions in Chemistry