Temperature Measurement: Instrument and Scales
Master Temperature Measurement: Essential Instruments, Scales & Conversions Explained | Selftution.com
Selftution.com is the best educational website for clear, simplified learning. Discover thermometers, Celsius vs Fahrenheit, Kelvin scale, and practical examples – all in one trusted guide. Welcome to smarter learning!
So, let’s begin.
Introduction to Temperature Measurement
When we place our hands in hot water, it feels hot, and when we touch ice, it feels cold. However, our sense of touch cannot accurately determine how hot or cold something is.
Therefore, we rely on temperature measurement to quantify the degree of hotness or coldness.
Skip to >> Instrument for measuring temperature
For example, when we feel hot water, it is because its temperature is higher than our body temperature. Conversely, touching ice feels cold because its temperature is lower than our body temperature.
This temperature difference creates the sensations of hotness or coldness.
Using precise instruments and scales, we can accurately measure these temperature differences, making it crucial for various applications in science, industry, and daily life.
Definition of temperature for kids –
The temperature is the measure of the degree of hotness or coldness of a body or environment. The standard international unit or SI unit of temperature is Kelvin (K).
Which instrument is to be used for the measurement of temperature?
Topics Covered:
THERMOMETER
To measure temperature, we use an instrument/device called a thermometer. There are various types of thermometers. However, the glass thermometer is one of the most common instruments used for measuring temperature.

The image depicts various parts of the clinical thermometer – the stem, capillary tube, glass bulb with mercury, and kink, which prevent backflow of mercury
This clinical or glass thermometer consists of a fine glass tube with a small bore, known as a capillary tube. One end of the tube contains a thin glass bulb holding mercury, and the other end is sealed after removing the air. A thicker glass tube called a stem encloses the delicate capillary tube for protection. The stem is marked with graduated degrees for reading the temperature. The stem is triangular, which helps magnify the markings when viewed, making it easier to read the temperature accurately.
Advantages of using mercury in a thermometer –
- It is opaque and shining. Hence, it is easily visible through the glass.
- It does not stick to or wet the glass.
- Mercury has a low freezing point (-39 °C) and a high boiling point (357 °C). Hence, we can use it over a wide range of temperatures.
- It is a good conductor of heat, so it quickly absorbs the temperature of the object.
- Mercury has a high coefficient of cubic thermal expansion. Hence, it helps in the measurement of even a slight change in the temperature of a substance or a body.
THERMOMETRIC SCALES FOR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT
To ensure accurate temperature measurement and avoid discrepancies caused by variations in markings on different thermometers, we use standard thermometric scales. The most popular temperature scales are Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. When calibrating a thermometer, we typically use the melting point of ice as the lower fixed point and the boiling point of water as the higher fixed point.
Celsius or Centigrade Scale
The temperature of a given body can be less than zero degrees Celsius. To express such temperatures, we place a minus sign before the number. For example, -10 °C or -100 °C. Conversely, the temperature of bodies like flame or boiling oil can be above 100 °C.
The Celsius scale, named after Swedish scientist Anders Celsius, is a commonly used scale for temperature measurement. The lowest point on this scale is zero, and we express it as 0oC (zero degrees Celsius). It corresponds to the melting point of the pure ice. Likewise, the highest point on this scale is one hundred, and we express it as 100 °C (100 degrees Celsius). It corresponds to the boiling point of pure water. For carrying out markings, we divide the length between these two points into 100 parts or divisions. Therefore, we also call this scale the centigrade scale, which means 100 degrees.
Fahrenheit Scale
The Fahrenheit scale is named after the German scientist G.D. Fahrenheit. We mostly use this scale for temperature measurement in clinical applications. The lowest point on this scale is 32°F (0 °C), which corresponds to the melting point of pure ice. Likewise, the highest point on this scale is 212°F (100 °C). It corresponds to the boiling point of pure water. This scale distributes the two reference temperatures into 180 degrees. As the number of divisions is greater on the Fahrenheit scale when compared to the Celsius scale, it offers more precise temperature measurement.

Inventor of Thermometer Scales – Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin
Kelvin or Standard International (SI) Scale
The standard international (SI) scale used for measuring temperature is the Kelvin scale, named after Lord Kelvin, a renowned Irish mathematician and physicist.
Temperatures can fall below zero degrees Celsius, but what is the lowest possible temperature? Lord Kelvin theoretically calculated this limit to be 273.15 degrees below zero degrees Celsius, naming it absolute zero. At absolute zero, the motion of all atomic and subatomic particles, including electrons, protons, and neutrons, ceases. Despite advancements in modern science, achieving absolute zero remains impossible.
The unit on the Kelvin scale is the same size as a Celsius degree and is called a Kelvin, abbreviated as K. To convert a temperature from Celsius to Kelvin, simply add 273.15 to the Celsius value. For example, 273.15°C equals 0 K, 0°C equals 273.15 K, and 100°C equals 373.15 K. It is important to note that Kelvin is not expressed in degrees.
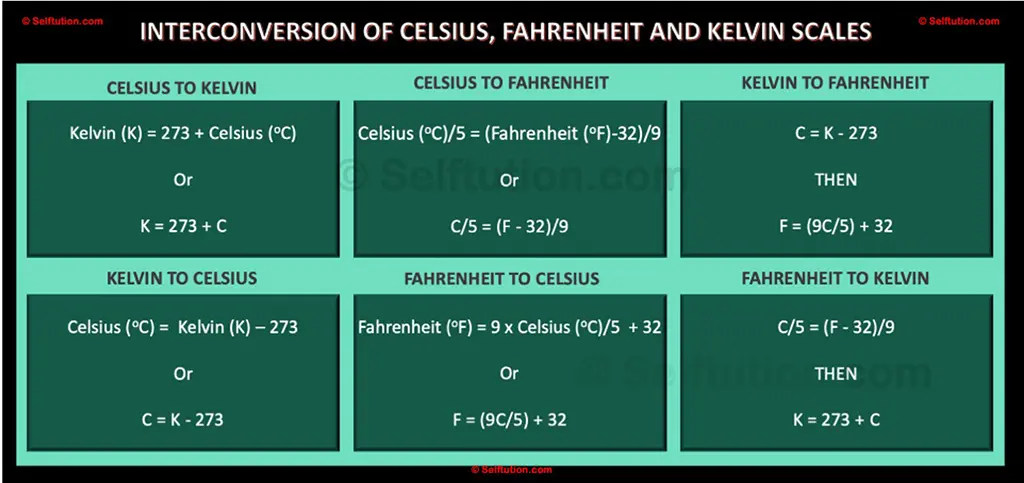
Temperature Scales, Celsius to Fahrenheit to Kelvin
OTHER INSTRUMENTS USED FOR TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT
Thermometers, or the instruments used for measuring temperature, are of various types:
Laboratory Thermometers
A laboratory thermometer is a type of glass thermometer designed for measuring temperatures in scientific and industrial settings, rather than the human body. It features a glass tube with a capillary bore and markings on its stem, typically ranging from -10°C to 110°C. The distance between two consecutive markings represents one degree Celsius, allowing for precise temperature readings.
The thermometer consists of a thin glass bulb at one end, which contains mercury or another suitable liquid. As the temperature changes, the liquid expands or contracts, moving up or down the capillary tube. This movement corresponds to the graduated markings on the stem, indicating the exact temperature.
Laboratory thermometers are essential tools in experiments, quality control processes, and various scientific applications where accurate temperature measurements are crucial. Their wide range and precise calibration make them ideal for environments where precise temperature control and monitoring are required.
Clinical Thermometer for Temperature Measurement
The temperature of a healthy person is 37 degrees Celsius. If the temperature is above 37 degrees Celsius, then the person is having a fever. However, if the temperature is less than 37 degrees Celsius, the person is weak and their body is not generating enough heat energy. A clinical thermometer is specifically designed to measure the temperature of the human body. It operates within a narrow range of 35°C to 42°C, as human body temperatures typically fall within these limits. The normal body temperature is around 37°C (or 98.6°F).
This thermometer features a triangular stem, which houses a very fine capillary tube. Near the bulb, there is a kink in the tube. This kink allows mercury to rise into the capillary tube when the temperature increases, but prevents it from flowing back down once the temperature drops. To reset the thermometer, a quick jerk is needed to return the mercury to the bulb.
It’s important to handle clinical thermometers with care. They should never be washed with hot water or exposed to direct sunlight, as these conditions can cause the glass to break. Proper maintenance ensures accurate readings and longevity of the instrument.
Six’s Thermometer
We use this instrument for the measurement of maximum and minimum temperatures attained during the day. It derives its name from its inventor, James Six, in 1972.
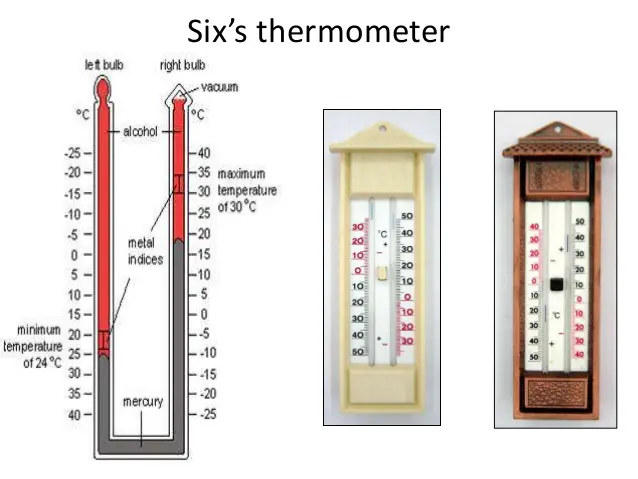
Six’s Thermometer with various parts
A Six’s thermometer, also known as a maximum-minimum thermometer, is designed for the measurement of both the highest and lowest temperatures over a period. It features a U-shaped tube with two separate scales for maximum and minimum temperature readings. At the top of each arm of the U-tube, there are bulbs: the left bulb contains alcohol, while the right bulb contains either a vacuum or low-pressure alcohol vapors. Mercury in the U-tube separates the alcohol from the vacuum.
Alcohol measures the temperature, while mercury indicates the readings on both scales. When the temperature rises, the alcohol in the left bulb expands, pushing the mercury down. This action causes the mercury to rise in the right arm, enabling the reading of the maximum temperature on the scale below the right bulb.
Conversely, when the temperature falls, the alcohol in the left bulb contracts. The mercury moves towards the left bulb to fill the resulting gap, enabling the reading of the minimum temperature on the scale below the left bulb.
As the mercury moves, it pushes two small steel markers inside the tube. These markers record the farthest points reached by the mercury in each arm of the tube. To reset the markers for reuse, a small magnet can be used to drag them along the tube back to the surface of the mercury.
Thermocouples for Temperature Measurement
A thermocouple is an electrical instrument used to measure temperature based on the Seebeck Effect. This effect occurs when a temperature gradient exists between two junctions made of dissimilar metallic wires, generating an electric current in the circuit. The voltage produced is directly proportional to the temperature difference between these junctions. Measuring this voltage allows the determination of the temperature at the measurement junction relative to the known temperature at the reference junction. Thermocouples utilize different metal combinations tailored for specific temperature ranges, allowing them to measure temperatures spanning from -270°C to 1300°C. They are widely employed in various industries due to their durability, fast response time, and ability to operate in harsh environments.
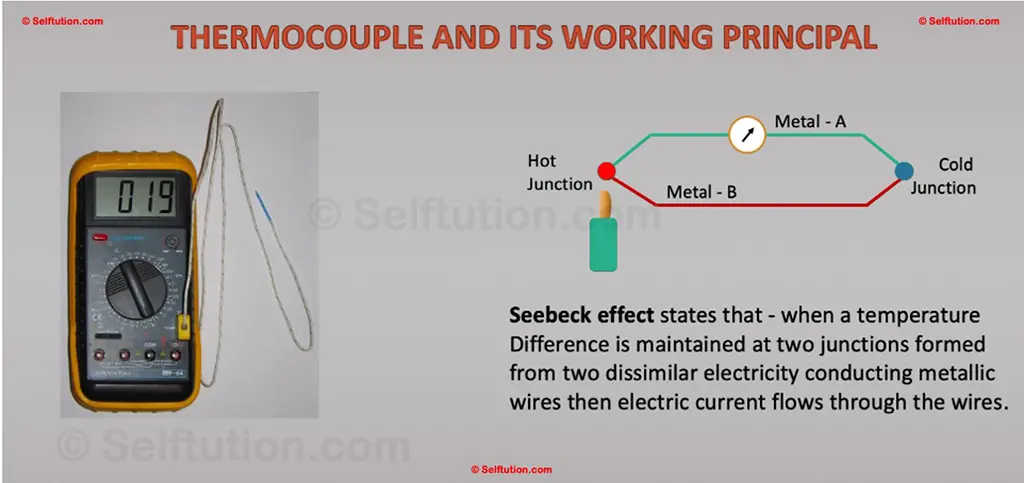
Thermocouple Working Principle
Thermistors
An electronic device, a thermistor, measures temperature by using changes in its electrical resistance with temperature variations. It operates based on the principle that its resistance decreases (NTC thermistor) or increases (PTC thermistor) with rising temperature. This change in resistance causes the voltage or electrical potential across the circuit to change correspondingly, allowing measurement of the temperature.
NTC thermistors exhibit an exponentially decreasing resistance with increasing temperature, which makes them sensitive and ideal for applications needing high sensitivity within a narrow temperature range. Engineers commonly employ them in temperature sensing and compensation circuits.
PTC thermistors, on the other hand, exhibit an increase in resistance to temperature, making them useful in applications where they can act as self-regulating heating elements or overcurrent protectors.
Thermistors are typically made from ceramic or polymer materials, providing operational temperature ranges typically from -55°C to +150°C. Specialized glass-body thermistors can operate up to +300°C. They are compact, reliable, and widely used in consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, and industrial equipment where precise temperature measurement and control are crucial.
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are temperature sensors that use the principle of electrical resistance of pure metals to measure temperature accurately. Unlike thermistors, which use ceramic or polymer materials, RTDs employ materials like platinum, nickel, or copper. The resistance of the RTD wire changes predictably with temperature, following a linear relationship. This characteristic allows RTDs to provide precise temperature measurements over a wide range.
Typically, an RTD consists of a fine wire wound around a ceramic or glass core to maintain stability and protect the wire. Due to their pure metal construction, RTDs are more stable and accurate compared to thermistors, especially in industrial and scientific applications where precise temperature control and measurement are essential. Industries commonly use RTDs in laboratories, industrial processes, and HVAC systems requiring robust and accurate temperature sensing.

Pyrometer or Infrared Thermometers
A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer or instrument used to measure the temperature of a surface from a distance. It determines the temperature of a surface from the amount of thermal radiation it emits, a process known as pyrometry. The picture depicts a sailor checking the temperature of a ventilation system using a pyrometer. Image courtesy Wikipedia.